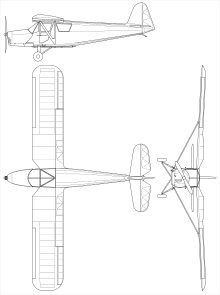
RWD-13
| RWD-13 | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Touring plane |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
January 15, 1935 |
| Production time: |
1935-1939 |
| Number of pieces: |
110 |
The RWD-13 was a Polish touring aircraft developed by the Warsaw-based manufacturer RWD in the mid-1930s .
development
Rogalski and Drzewiecki constructed the RWD-13 as the successor to the RWD-6 and RWD-9 , which had been specially developed for the Challenge de Tourisme International in 1932 and 1934 , respectively. Like this, the RWD-13 was a strutted shoulder- wing aircraft with a rigid landing gear and slats . For the purpose of use as a touring aircraft, however, a weaker drive and places for two passengers were provided.
The first flight took place on January 15, 1935 and resulted in a number of orders. In addition to the main part of the RWD-13 produced for Polish aero clubs, around 20 aircraft were exported. They flew u. a. in Brazil, Estonia, Yemen, Austria, the USA and Venezuela. One copy was given to the Shah of Persia as a birthday present from the Polish government. Four planes flew liaison missions on the side of the Franco troops in the Spanish Civil War . Two RWD-13s ( VQ-PAL and VQ-PAM ) were purchased in 1939 from the Palestine-based Aviron company that used them for pilot training. As recently as 1948, you flew missions on the side of Israel during the Palestine War. After the attack on Poland began , a number of RWD-13s were requisitioned by the Polish army. In the further course of the war, about 25-40 aircraft were withdrawn from German access by being transferred to Romania. 21 survived the end of the war there and four of them were then returned to Poland, which they used for a few years.
In 1937 fifteen copies of the medical version RWD-13S appeared . Yugoslavia produced both the RWD-13 and the RWD-13S under license.
One RWD-13 is located in the Polish Aviation Museum and one in the Museu da TAM in São Carlos , Brazil.
construction
The RWD-13 was a shoulder-wing monoplane in mixed construction. The fuselage consisted of fabric-covered tubular steel with a rectangular cross-section. The two front seats had dual controls , the third seat was behind and was accessible through a separate door. The braced wing had two spars , flaps and slot ailerons . It consisted of a wooden frame and was paneled with plywood in the front area and covered with fabric behind it. The two fuel tanks with a total volume of 140 l were also housed in it. The tail unit was self-supporting and was also made of wood with plywood and fabric. The chassis was rigid, had an hydropneumatic suspension and had a tail spur .
Military users

-
 Brazil
Brazil
- Brazilian Air Force
-
 Estonia
Estonia
- Estonian Air Force 1 copy
-
 Croatia
Croatia
- Air Force of the Independent State of Croatia, 1 copy of the former Royal Yugoslav Air Force
-
 German Empire
German Empire
- Luftwaffe some copies
-
 Israel
Israel
- Israeli Air Force 2 copies
-
 Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia
- Yugoslav Air Force, 4 copies
-
 Poland
Poland
- Polish Air Force
-
 Romania
Romania
- Romanian Air Force
-
 Sweden
Sweden
- Swedish Air Force 1 copy from 1939 for evaluation as Tp 11
-
 Spain
Spain
- Spanish Air Force
Technical specifications
| Parameter | Data |
|---|---|
| crew | 1-2 |
| Passengers | 1-2 |
| Wingspan | 11.50 m |
| length | 7.85 m |
| height | 2.05 m |
| Wing area | 16.0 m² |
| Wing extension | 8.3 |
| drive | a Gipsy Major I in- line engine with 97 kW (132 PS) |
| Tank volume | 140 l |
| Top speed | 210 km / h near the ground |
| Cruising speed | 187 km / h |
| Landing speed | 60 km / h |
| Climb performance | 3.4 m / s |
| Rise time | 4.4 min at 1000 m altitude |
| Service ceiling | 4200 m |
| Range | 900 km |
| Empty mass | 530 kg |
| Payload | 360 kg |
| Takeoff mass | normal 890 kg maximum 930 kg |
| Wing loading | 55.6 kg / m² |
| Power load | 6.8 kg / hp |
| Area performance | 8.1 hp / m² |
literature
- Wilfried Copenhagen , Jochen K. Beeck: The large aircraft type book . Motorbuch, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 978-3-613-02522-6 , p. 508 .
- Peter Alles-Fernandez (Ed.): Aircraft from A to Z. Volume 3: Koolhoven FK 56 - Zmaj. Bernard & Graefe, Koblenz 1989, ISBN 3-7637-5906-9 .
- Heinz A. F. Schmidt: Historical Aircraft I . Transpress, Berlin, p. 127 .
- Werner von Langsdorff : Handbook of aviation . Born in 1939. 2nd, unchanged edition. J. F. Lehmann, Munich 1937, p. 486 .
- Andrzej Glass: Polskie Konstrukcje lotnicze 1893-1939 (Polish aviation constructions 1893-1939) . WKiŁ, Warsaw 1977, p. 313-318 (Polish).
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ J. Fernandez, P. Laureau, A. Yofe: Between Purchase and Conspiracy - The History of the Development of the Israeli Air Force - Part 1. In: Fliegerrevue Extra No. 30. Möller, Berlin 2010, p. 10