Rescue Sports
The rescue sport developed in many countries, mostly from the same idea: lifeguard training and mutually compete in competitions. Initially in Australia in open water competitions, similar disciplines for indoor swimming pools developed elsewhere . In Germany, the German Life Rescue Society (DLRG) mainly promotes the development of rescue sports. The International Life Saving Federation (ILS) made it possible to establish an internationally standardized set of rules for the implementation of worldwide lifeguard competitions. The sporting development does not stop at this former fringe sport. This sport has not only become a trend sport, but competitive and top-class sport has also developed into world championships such as rescue .
The disciplines
Competitions in rescue swimming are traditionally divided into two types: first, the disciplines in the swimming pool (in English usually works best pool events ) and on the other disciplines in the open water ( open water ). The variety of disciplines ranges from regional rescue comparison competitions, in which the lowest level of a water rescue organization can freely define competition disciplines, to strictly regulated implementation provisions at state and federal level and international competitions.
As a new sport, the IRB competitions developed in the first decade of the 21st century, in which teams train to rescue people from the surf zone with inflatable rescue boats specially developed for surf rescue.
Swimming pool disciplines
The swimming pool disciplines are very widespread in Germany. The water rescue organizations of the ASB, the DLRG and the DRK set their own regulations for the implementation of lifeguard competitions.
Individual disciplines
- 200 m obstacle swim
The competitor swims 200 m freestyle after the start . During this discipline a 70 cm deep obstacle has to be submerged eight times.
- 50 m rescuing a doll (manikin carry)
Swim 25m freestyle, then dive to a doll. This must be brought to the surface of the water within a distance of five meters and dragged the rest of the way to the destination.
- 100 m combined rescue exercise (Rescue Medley)
50 m freestyle, turning and diving to a manikin 17.5 m away. Drag the doll to the finish.
Swim 50 m freestyle with flippers, then dive to a doll, bring it to the surface and drag it to the finish.
- 100 m rescue with fins and belt rescuer (Manikin Tow with Fins)
Swim 50 m freestyle with flippers and harness rescuer. At the turn mark of a doll, put on the safety belt and pull it 50 m to the target.
- 200 m Super Lifesaver
Swim 75 m freestyle, dive to a water-filled doll at the 75-meter mark and bring it to the surface. Drag 25 m of the doll , put on the harness and fins at the 100-meter mark and swim 50 m to another doll. Drag this 50 m with the belt rescuer.
- 100 m rescue by boat (lifesaving by boat)
Row the boat to a buoy , circle it, then row to a doll lying in the water. Pull this up to the edge of the boat and cover the rest of the way with just one strap.
Team disciplines
- 4 × 25 m doll relay (Manikin Relay)
All four relay swimmers drag the rescue manikin 25 m each.
- 4 × 50 m obstacle relay
Four athletes swim 50 m freestyle each and submerge an obstacle twice.
- 4 × 50 m belt rescue relay (Medley Relay)
The relay consists of four competitors. The 1st swimmer swims 50 m freestyle. The second swimmer covers the same distance with flippers. The 3rd swimmer swims 50 m freestyle with the harness belt wrapped around his shoulder. He then hands this over to the 4th swimmer, who then tows the 3rd swimmer 50 m with fins and with the help of the belt rescuer.
- 4 × 50 m rescue team
This relay consists of four swimmers who cover the distance of 50 m one after the other. The starting swimmer swims 50 m freestyle with flippers. The 2nd swimmer dives 25 m with fins, swims 25 m freestyle with fins and retrieves the rescue manikin for the third swimmer from the bottom of the pool. The 3rd swimmer then tows it 50 m and then passes the doll to the 4th swimmer, who then tows the doll with fins.
- Line-throwing (Line Throw)
A lifeguard stands at the edge of the pool and rescues a victim who is 12.5 m from the edge of the pool within a time limit of 30 seconds. After the start signal, the rescuer fetches the rope held by the victim and throws it back to the victim. The victim has to grab the rope and is pulled back to the edge of the pool by the rescuer.
- Simulated Rescue Exercise (SERC)
Accident scenario with 7 to 14 "victims" in and around the water. Different emergency situations are presented. A team of 4 lifeguards comes to the rescue, has to recognize and evaluate the situation and should help as many victims as possible within 2 minutes.
Open water disciplines
History of the Open Water Disciplines
The open water disciplines have their origins in New Zealand and Australia . Such competitions have been held there at a high level for decades. Rescue sport is a popular sport there and is broadcast on television. The television series Baywatch made this type of rescue sport popular in Germany, and so the first open water competition was held by the DLRG in 1994. As early as 1990, the rescue (world championship) was held by the DLRG in Lübeck / Travemünde (with pool and open water competitions).
Individual disciplines
- Surf Swimming (Surf Race)
There is a circular course of approx. 400 m to swim. Start and finish are at the water's edge.
- Rescue Board Race
The competitors start with the Rescue Board ( rescue board ) at the water edge. You move with your arms lying down or kneeling on the board. A round course of approx. 600 m has to be completed.
- Rescue Ski Race (Surf Ski Race)
On the surf ski (rescue kayak), a circuit of approx. 700 m must be circumnavigated using a paddle . This is the fastest form of muscle- powered locomotion for the rescue athlete.
- Lifeguard (Oceanman / Oceanwoman)
In this supreme discipline, the rescue athlete completes the surf swim (300 m), the rescue board (400 m) and the rescue ski race (500 m) one after the other. The order will be drawn before the competition. In order to distinguish it from the triathlon Ironman , this discipline has been called Oceanman / Oceanwoman since 2006 and no longer Ironman / Ironwoman.

- Beach flags
At the start of this event, all competitors lie on their stomachs with their feet on the starting line in the sand. In response to the start signal, one of the bars 20 m away is taken. Since there is one less staff than participants, one athlete is eliminated after each round. This discipline, which focuses on the ability to concentrate, react and sprint, is similar to the children's game Journey to Jerusalem .
- Beach sprint ( beach sprint)
90 m sprint in the sand.
Team disciplines
- Rescue with belt rescuer (Rescue Tube Rescue Race)
A team consists of four athletes (a fin swimmer, a victim and two helpers). After the start signal, the victim swims to a buoy and signals with a hand signal that he has arrived. At the signal, the fin swimmer grabs his fins and the belt rescuer, sprints into the surf and puts on both. He then swims to the buoy and puts the belt rescuer on the victim. The fin swimmer drags the victim back to the beach. The rescue is supported by the two helpers, who can meet the lifeguard in waist-deep water, take over the victim and drag them across the finish line at the stand.
- Rescue with a rescue board (Rescue Board Rescue Race)
This discipline is completed by two competitors. After the start signal, the first one swims to his buoy and signals his arrival with a hand signal. The second then starts with the lifeboat and picks up the swimmer on the buoy. Together they paddle on the lifeboat to their destination on the beach.
- Mixed Rescue Relay Race (Taplin Relay Race)
Four competitors each complete one of the disciplines of the Oceanman / Oceanwoman in relay form. The order of the disciplines will be drawn.
- Beach sprint relay (Beach Relay)
4 competitors sprint each 90 m in the sand.
IRB disciplines
The four disciplines of the IRB competitions simulate the rescue of one or more people from the surf zone on the beach with the help of the so-called Inflatable Rescue Boats (IRB) specially developed for this purpose .
- Rescue Event
A crew consists of a boat operator, lifeguard and a "patient". The patient is in a fixed position in the water and is brought to shore by the crew as quickly as possible.
- Mass Rescue Event
A crew consists of a boat operator, lifeguard and two "patients". The patients are in a fixed position in the water and are brought to the bank one by one by the team as quickly as possible. The first patient is not allowed to help his teammates prepare for the rescue of the second after leaving the boat.
- Team Rescue Event
A crew consists of two boatmen, two lifeguards and two "patients". Both patients are in a fixed position in the water. The first is brought ashore by the first team as quickly as possible. On the beach, the skipper changes the relay to the second skipper. The first lifeguard stays with the boat until the second crew takes over. This may only start for the second patient when the first lifeguard has also reached the transition area. The second team then rescues the second patient. The first patient is not allowed to help his teammates prepare for the rescue of the second after leaving the boat.
- Rescue Tube Event
A team consists of a boat operator, a lifeguard (with a lifebelt) and a "patient". The patient is in a fixed position in the water. During the rescue, the lifeguard jumps into the water and uses the belt lifter he is carrying to secure the patient and pull him to the boat. There the skipper helps him pull the patient into the boat. Then the boat will return to shore as soon as possible.
The DLRG competition system in Germany
The German competition system for indoor rescue sports is written down in the DLRG regulations. Competitions take place regularly at all levels of the DLRG. Many local groups regularly organize friendship competitions within the districts and district associations in order to compete with other local groups. Many local groups also hold club championships. District championships can take place once a year in each district, at which lifeguards from all local groups in the respective district can qualify as teams and individual starters for the state championships. These are organized by the regional association. There, in turn, the best teams and swimmers qualify for the German Championships of the DLRG, at which the respective German champion is determined.
The competition system of the DLRG is divided into the age classes AK 12, AK 13/14, AK 15/16, AK 17/18, AK open and within these age groups according to sex. Lifeguards can start alone or in a team consisting of four to five swimmers. The disciplines in the individual starts include obstacle swimming, a rescue exercise with and without fins and a rescue exercise with a belt lifter and fins. The routes are 50 m to 200 m long, depending on the age group. Team disciplines largely correspond to the individual disciplines, but are swum as a relay and swim 4 × 25 m to 4 × 50 m.
The DLRG Service Gesellschaft mbH (DSG) organizes open water competitions during the summer. The DLRG Cup is held annually in Warnemünde and is the largest open water event in Germany. Athletes from many European nations and many German club teams compete at this event. The DLRG Trophy is an open water series usually consisting of three competitions that are held at different locations in the Federal Republic. The individual results are summarized in a daily evaluation and at the end there is a final table.
The international competition system of the ILS
- The global umbrella organization for rescue sports, the International Life Saving Federation (ILS), holds world championships every two years . There are different subspecies. Participation is open to national teams , club teams (a club corresponds to a German local branch), and seniors (Masters).
The last world championship in Germany took place from July 20 to 29, 2008 in Berlin and Warnemünde and was organized by the DLRG. The last World Cup was held in Adelaide (Australia) in 2018 . The 2020 World Cup will take place in Riccione (Italy). - ILS-Europe ( ILS-E ) also holds European championships every two years. There are also competitions for juniors there. The 2013 European Championship in lifeguarding took place from August 16 to 18, 2013 in The Hague , the Netherlands. Before that, the European Championship was held from September 15 to 19, 2011 in Alicante , Spain. The 2015 European Championship was held in Wales, the 2017 European Championship in Belgium. In 2019 the EM will take place in Riccione (Italy).
- Rescue sports have also been an integral part of the World Games since 1985 , which are held every four years at different locations. The World Games took place from July 25 to August 9, 2013 in Cali , Colombia . Marcel Hassemeier , who was part of the German national team, was the most successful athlete of the World Games with 4 × gold and 1 × silver and was also voted "Athlete of the Year" 2013. In 2017 the World Games took place in Wroclaw, Poland.
Swimming pool at the national and international championships
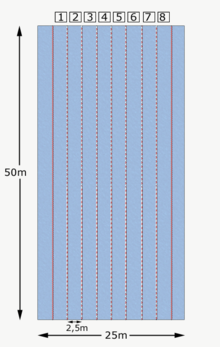
A swimming pool in the Rescue , European and German championships must meet special criteria so that the same conditions prevail in all sports facilities and a better international comparison can take place. For this reason, the bathrooms should also be covered with a solid roof. The characteristics of a competition pool are as follows:
| Length: | 50 m |
| Swimming lane width: | 2.5 m |
| Water temperature: | 25-28 ° C |
If electronic stop fields are used, the length between them must still be 50 m (they must not protrude into the pool). The accuracy requirements for the pool length are high, since a length difference of 1 cm in a 100 m freestyle leads to a time difference of 1/100 of a second. For this reason, the time measurement to the thousandth of a second, which was used in the 1972 Olympic Games, was abolished.
In addition, there are black lines along the lanes on the bottom of the pool, so that the swimmers can orientate themselves better when swimming in the chest position.
The competition equipment
- Belt Rescuer (Rescue Tube)
- Competition fins
- Obstacle in obstacle swimming
- Competition manikin
- Paddle Board (Malibu Board)
- Surf skis
- IRB
athlete
See also
Web links
- Video of the Rescue 2008
- Official website of the 2012 World Cup
- Result of the German national team at the World Games 2013
- Official website of the 2014 World Cup
- private German-speaking rescue sports site
- private German-speaking rescue sports website (Switzerland)
- Rescue sports area of the DLRG
- Pages of the German Lifeguard Championships of the DLRG
- Official website of the International Life Saving Federation (ILS)
Individual evidence
- ↑ International regulations from 2013 on: www.ilsf.org/lifesaving-sport/rules, accessed on January 2, 2014
- ↑ Rescue sport swimming pool disciplines on: www.dlrg.de, accessed on January 2, 2014
- ^ History of rescue sports; The rescue sport disciplines ( Memento from January 4, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) On: www.dlrg.de, accessed on January 2, 2014
- ↑ Rescue sports open water disciplines on: www.dlrg.de, accessed on January 2, 2014
- ↑ Disciplines IRB at: www.dlrg.de, accessed on January 2, 2014
- ↑ Rescue sport DLRG rules at: www.dlrg.de, accessed on January 2, 2014
- ↑ World Games website, accessed on February 2, 2014