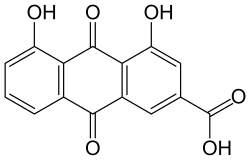
Rhine (Anthranoid)
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Rhine (Anthranoid) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 8 O 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
orange needles |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 284.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Sublimation point |
321 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Rhine (pronunciation: Rhe-in ) is a chemical compound from the group of anthranoids , which is formed by the polyketide route .
Occurrence
Rhine occurs both free and in the form of β- D - glucosides as well as dimers ( sennosides ) in the roots of Rheum palmatum (medicinal rhubarb) and the meadow sorrel and in Senna alexandrina ( senna leaves).
use
Rhein-1,8-diacetate in particular is used as a laxative and anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of arthritis .

