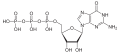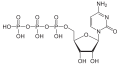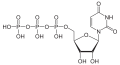Ribonucleotides
Ribonucleotides are the building blocks of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Together with the deoxyribonucleotides , they belong to the nucleotides . Ribonucleotides consist of a nucleoside in which the sugar D - ribose, with one of the nucleobases - such as the purine bases adenine (A) and guanine (G) or the pyrimidine bases cytosine (C), uracil (U) and rarely thymine ( T) - is linked, as well as a phosphate residue .
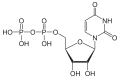
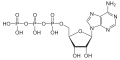
Monophosphates
In the food industry, mixtures of ribonucleotides with a phosphate group (nucleoside monophosphate, NMP) are used as flavor enhancers and declared as calcium 5′-ribonucleotide (E 634), disodium 5′-ribonucleotide (E 635):
Adenosine monophosphate
(AMP)Guanosine monophosphate
(GMP)Cytidine monophosphate
(CMP)Uridine monophosphate
(UMP)
Diphosphates
The natural nucleoside diphosphates (NDP) are:
Adenosine diphosphate
(ADP)Guanosine diphosphate
(GDP)Cytidine diphosphate
(CDP)Uridine diphosphate
(UDP)
Triphosphates
The natural nucleoside triphosphates (NTP) are:
Adenosine triphosphate
(ATP)Guanosine triphosphate
(GTP)Cytidine triphosphate
(CTP)Uridine triphosphate
(UTP)
literature
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer : Biochemie , 6th edition, Spectrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2007, ISBN 978-3-8274-1800-5 .
- Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet: Biochemistry , 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, New York 2004, ISBN 0-471-19350-X .
- Bruce Alberts , Alexander Johnson, Peter Walter, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts: Molecular Biology of the Cell , 5th Edition, Taylor & Francis 2007, ISBN 978-0-81534106-2 .