Pink fedchenkoana
| Pink fedchenkoana | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Pink fedchenkoana |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Pink fedchenkoana | ||||||||||||
| rule |
Pink fedtschenkoana is a plant from the genus roses ( Rosa ) within the family of the rose family (Rosaceae). She comes from Central Asia .
Rosa fedtschenkoana was discovered by Olga Alexandrovna Fedtschenko on a trip through Central Asia in Turkestan and brought to Saint Petersburg. The German botanist Eduard August von Regel first described this type of rose in 1878 and dedicated it to the discoverer. DNA tests have shown that Damascus roses as well as Remontant and moss roses are descended from Rosa fedtschenkoana . This clarifies where the remontant genes of western roses come from.
description
Vegetative characteristics
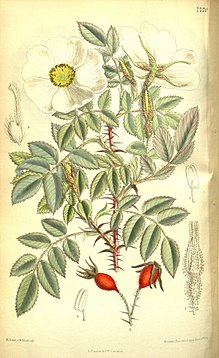
Rosa fedtschenkoana forms a large shrub that spreads through runners with "root shoots" and can therefore grow up to 6 meters wide and reach heights of up to 2.5 meters. The bark of young twigs is whitish and densely covered with initially carmine-red, long spines . The stem-round branches are provided with up to 7 millimeters long, straight, yellowish, stiff spines that gradually widen towards their base.
The alternate leaves are arranged in petioles and petioles and are 3 to 4.5 centimeters long. The imparipinnate leaf blades are gray-green with usually seven, rarely five or nine leaflets. The leaflets are almost circular or ovoid with an almost rounded or broadly wedge-shaped base and a rounded, blunt upper end. The leathery leaflets have raised leaf veins on the underside. The leaf margin is simply serrated, but not serrated in the lower area. The leaf hachis and the petioles are glabrous or hairy sparsely glandular and downy. The stipules are fused with the petiole over almost their entire length; its free part is lanceolate to ovate with a pointed upper end and its edge is hairy with glandular hairs.
Generative characteristics
Rosa fedtschenkoana blooms continuously from early summer into autumn; in Xinjiang from July to August. The flowers are usually solitary, rarely in pairs to four in bundles. The flower stalk is 1 to 2 inches long and downy with stalked glandular hairs. The bracts are ovate or ovate-lanceolate with a tailed upper end and downy with glandular hairs.
The hermaphrodite, unpleasantly scented flowers have a diameter of 3 to 4 centimeters and are radially symmetrical and five-fold with a double flower envelope . The egg-shaped flower cup (hypanthium) has stalked glands or is rarely bare. The five sepals are lanceolate with a pointed upper end and their underside is densely hairy. The five white, rarely pink petals are broadly obovate with a broad, wedge-shaped base and a chipped upper end. There are many stamens present. The free styles are shorter than the stamens and hairy downy.
The rose hips, which are brightly red when ripe, are elongated to egg-shaped or pear-shaped and have a diameter of 1.5 to 2 centimeters. The five durable sepals are located on the glandular, downy, hairy rose hip. In Xinjiang, the rose hips ripen from August to October.
distribution
Rosa fedtschenkoana is common in Central Asia in Kazakhstan and the Xinjiang Autonomous Region, which is part of the People's Republic of China . In Xinjiang it thrives in bushes, on slopes and on the banks of flowing waters in valleys at altitudes of 2,400 to 2,700 meters.
Systematics
The first description of Rosa fedtschenkoana was made in 1878 by Eduard August von Regel in Trudy Imperatorskago S. Peterburgskago Botaničeskago Sada , Volume 5, 2, pp 314-315. The specific epithet fedtschenkoana honors the German-Russian naturalist Olga Fedtschenkoi (1845–1921). Synonyms for Rosa fedtschenkoana are usually : Rosa caraganifolia Sumnev. , Rosa coeruleifolia Sumnev. , Rosa epipsila Sumnev. , Rosa lavrenkoi Sumner , Rosa lipschitzii Sumner , Rosa oligosperma Sumnev. Sumner , Rosa minusculifolia . Some botanists see this wild rose as a subspecies of Rosa beggeriana , others refer to it as Rosa webbiana Wall. ex Royle .
Rosa fedtschenkoana belongs to the series Webbianae from the section Rosa in the subgenus Rosa within the genus Rosa .
use
The rose is frost hardy to -35 ° C ( USDA zone 4 ). The rose hips are used and contain up to 6.6% ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in the dry matter .
swell
literature
- Gu Cuizhi, Kenneth R. Robertson: Rosa. Pink fedchenkoana. P. 367 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China. Volume 9 - Pittosporaceae through Connaraceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2003, ISBN 1-930723-14-8 .
- Charles Quest-Ritson, Brigid Quest-Ritson: Roses: The Great Encyclopedia. The Royal Horticultural Society, translation by Susanne Bonn; Dorling Kindersley, Starnberg 2004, ISBN 3-8310-0590-7 , p. 147.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Gu Cuizhi, Kenneth R. Robertson: Rosa. Pink fedchenkoana. P. 367 - online with the same text as the printed work , In: Wu Zheng-yi, Peter H. Raven (Ed.): Flora of China. Volume 9 - Pittosporaceae through Connaraceae , Science Press and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, Beijing and St. Louis, 2003, ISBN 1-930723-14-8 .
- ↑ Rosa fedtschenkoana in the Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN), USDA , ARS , National Genetic Resources Program. National Germplasm Resources Laboratory, Beltsville, Maryland. Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Eduard August von Regel, scanned in at biodiversitylibrary.org in 1878 .
- ↑ Entry in World of Roses .
- ↑ a b Rosa fedtschenkoana at Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, Retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ↑ Rosa fedtschenkoana at Plants For A Future . Retrieved November 18, 2017.
Web links
- World of roses .
- USDA data sheet.
- Jingyun Fang, Zhiheng Wang, Zhiyao Tang: Atlas of Woody Plants in China: Distribution and Climate, Volume 1 . Springer Science & Business Media, 2011, ISBN 978-3-642-15017-3 , pp. 556 ( Distribution of Rosa fedtschenkoana in China on p. 556 in the Google book search).
- Datasheet at Rosa Database .
- Datasheet at deeproot.co.uk .