Selamectin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
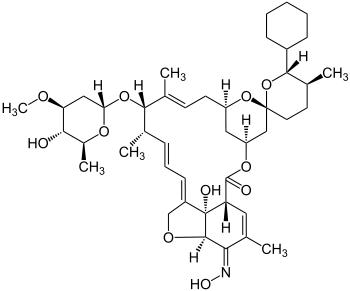
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Selamectin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
25-Cyclohexyl-4'- O -de (2,6-dideoxy-3- O- methyl-α- L -arabino-hexopyranosyl) -5-demethoxy-25-de (1-methylpropyl) -22,23-dihydro -5- (hydroxyimino) -avermectin A1a |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 43 H 64 O 10 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Increase of the membrane permeability for chloride |
|||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 769.96 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Selamectin is an active ingredient from the group of macrocyclic lactones ( macrolides ) or avermectins , which is often used in veterinary medicine to combat parasites .
Mechanism of action
Selamectin is effective against both roundworms and ectoparasites ( insects and mites ). Like all avermectins selamectin increases the membrane permeability of the nerve cells in nematodes or the nerve and muscle cells in arthropods for chloride - ions . This takes place through binding to glutamate- activated chloride channels, which are highly specific for invertebrates , which leads to hyperpolarization of the cell membrane and blockage of the conduction of excitation. This leads to a complete paralysis of the parasites and thus to their death.
Selamectin also has an ovocidal effect (kills worm eggs) in worms, while egg formation is strongly suppressed in ticks and fleas .
In higher doses (above the normal therapeutic), selamecin also attacks GABA-mediated chloride channels and potentiates the effect of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Since these channels are also found in vertebrates, side effects can occur here.
According to Dryden, selamectin has a far-reaching effect. For example, treating a house cat kills larvae, eggs and fleas living in its home environment: Fleas release their excrement on the host, which falls off when cleaning with the flea eggs. The larvae, which develop from the eggs and sit in the carpet or other floors, feed on the droppings that have fallen off during cleaning and perish as a result. Therefore, selamectin works even in the cat's environment and also clears the environment of parasites.
application
Selamectin may only be used topically, i.e. only applied to the skin. It spreads over the fur within half a day. While in dogs the agent is hardly absorbed through the skin , in cats it is also absorbed into the bloodstream. The plasma half-life is 11 days in dogs and 8 days in cats. Applying it to the mucous membranes must be avoided at all costs; if it comes into contact with the eye , immediately rinse with plenty of water.
In contrast to the related active ingredient ivermectin , selamectin is also tolerated in dogs with the MDR1 defect . Side effects practically never occur when used properly. Seldom vomiting , unwillingness to eat , diarrhea , lethargy and increased salivation can occur in dogs , and in cats a temporary, slight muscle tremor.
The product must not be used in young animals (<6 weeks) or in the case of heartworm disease .
Trade names
- Monopreparations
Selehold , Stronghold , Revolution
- Combination preparations
- with Sarolaner : Stronghold Plus
Web links
- Entry on selamectin at Vetpharm, accessed on November 7, 2019.
Individual evidence
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A labeling of (2aE, 4E, 5′S, 6S, 6′S, 7S, 8E, 11R, 13R, 15S, 17aR, 20aR, 20bS) -6′-cyclohexyl-7- is shown, which is derived from a self-classification by the distributor [(2,6-dideoxy-3-0-methyl-α-1-arabinohexopyranosyl) oxy] -3 ', 4', 5 ', 6,6', 7,10,11,14,15,20a, 20bdodecahydro -20b-hydroxy-5 ', 6,8,19-tetramethylspiro (11,15-methano-2H, 13H, 17H-furo [4,3,2-p, q] [2,6] benzodioxacyclooctadecine-13.2 ′ - [2H] pyran) -17.20 (17aH) -dione 20-oxime in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on January 20, 2019.
- ^ MW Dryden and AB Broce: Integrated flea control for the 21st Century. In: Comp. Cont. Ed. Pract. Vet. 24: 1 suppl. 36-39, 2002.