Semliki Forest Virus
| Semliki Forest Virus | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
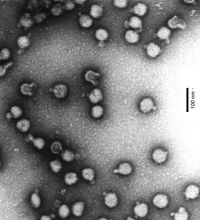
Semliki Forest Virus: intact and burst virions in the TEM image |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomic characteristics | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Semliki Forest Virus | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Short name | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SFV | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Left | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Semliki Forest virus (SFV) is a in rodents occurring alphavirus from the family Togaviridae , the by mosquitoes of the genus Culex as a vector is transmitted. It was isolated from these for the first time in 1942 in Uganda in the neighboring forest areas of the Semliki River .
The genome of the SFV is a linear, single-stranded RNA with positive polarity that contains two open reading frames for the structural and non-structural proteins. At the 5 'end of the RNA is a cap structure and a 3' end poly-A tail . Without the flanking, terminal section, the SFV genome comprises 11,442 nucleotides . The two envelope proteins E1 and E2 are regularly linked to the icosahedral capsid via transmembrane domains , so that the virus envelope has a regular structure. The complete virion of the SFV is about 70 nm in diameter, the capsid about 40 nm and shows a symmetry with a triangulation number of T = 4.
Biological properties
The SFV is widespread in East , Central and South Africa , to a lesser extent in India and Southeast Asia, where it is transmitted to smaller rodents by chronically infected mosquitoes. Some isolates of the SFV can cause encephalitis in rodents, which is fatal. Infection can also occur experimentally through aerosols via the nasal mucous membrane; natural infection occurs only through insect bites. The SFV does not cause any characteristic disease in humans. If the course is largely symptom-free, a slight fever can occasionally occur. In only one case has a fatal course as a result of SFV encephalitis been described, in which a highly concentrated cell culture supernatant caused an unnatural infection by aerosols in laboratory experiments. An Asian subtype provisionally assigned to the SFV species is the Me Tri virus, the genome of which is not fully known and which can possibly cause a febrile illness in humans.
Due to its relative apathogenicity, the SFV is also used for the production of viral vectors in genetic engineering or for gene therapy .
Individual evidence
- ↑ ICTV Master Species List 2018b v1 MSL # 34, Feb. 2019
- ↑ a b c d ICTV: ICTV Master Species List 2019.v1 , New MSL including all taxa updates since the 2018b release, March 2020 (MSL # 35)
- ^ Willems WR et al .: Semliki forest virus: cause of a fatal case of human encephalitis . Science (1979) 203 (4385): pp. 1127-1129 PMID 424742
- ↑ DQ Ha et al .: Isolation of a newly recognized alphavirus from mosquitoes in Vietnam and evidence for human infection and disease . American J. Trop. Med. Hyg. (1995) 53 (1): pp. 100-104 PMID 7625527
- ↑ K. Lundstrom: Semliki Forest virus vectors for gene therapy . Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. (2003) 3 (5): pp. 771-777 (Review) PMID 12880377
literature
- David M. Knipe, Peter M. Howley, et al. (eds.): Fields' Virology, 4th Edition, Philadelphia 2001
- CM Fauquet, MA Mayo et al .: Eighth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses , London, San Diego, 2004