East Africa
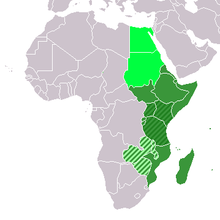
As East Africa are the eastern countries of the African continent called, with different geographical or political definitions.
East Africa
General
In East Africa, tour operators often only refer to the safari areas of Kenya , Uganda and Tanzania due to the tourist interest .
The geographical area of East Africa shows great cultural heterogeneity. Even if one can refer to a representative, homogeneous cultural tradition on the coast, the Swahili social form, which was influenced by Eastern Arabia and India , the most diverse ethnic groups cavort in the coastal hinterland in a very small area. In addition to the eastern bantu , there are also descendants of the Cushites , Nilots and San , the so-called Bushmen. Even though the Swahili coastal society has long since passed its heyday, Swahili as a language is the dominant medium in the area, especially around the great lakes .
Geographically
The geographical definition includes the region roughly east of the Nile or east of the East African Rift Valley . A restricted definition limits East Africa to the area east of the East African Rift Valley between Ethiopia and the Rovuma River , which includes the countries Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Burundi and Rwanda . Sometimes parts of Mozambique , Malawi and Sudan are added.
Political structure

In the statistics department of the UN , the following 20 countries are listed under East Africa under the Eastern Africa statistical district as of October 2013 :
-
 Ethiopia (capital Addis Ababa )
Ethiopia (capital Addis Ababa ) -
 Burundi (capital Gitega )
Burundi (capital Gitega ) -
 Djibouti (capital Djibouti (city) )
Djibouti (capital Djibouti (city) ) -
 Eritrea (capital Asmara )
Eritrea (capital Asmara ) -
 Kenya (capital Nairobi )
Kenya (capital Nairobi ) -
 Comoros (capital Moroni )
Comoros (capital Moroni ) -
 Madagascar (capital Antananarivo )
Madagascar (capital Antananarivo ) -
 Malawi (capital Lilongwe )
Malawi (capital Lilongwe ) -
 Mauritius (capital Port Louis )
Mauritius (capital Port Louis ) -
 Mayotte (capital Mamoudzou )
Mayotte (capital Mamoudzou ) -
 Mozambique (capital Maputo )
Mozambique (capital Maputo ) -
 Réunion (capital Saint-Denis )
Réunion (capital Saint-Denis ) -
 Rwanda (capital Kigali )
Rwanda (capital Kigali ) -
 Zambia (capital Lusaka )
Zambia (capital Lusaka ) -
 Seychelles (capital Victoria )
Seychelles (capital Victoria ) -
 Zimbabwe (capital Harare )
Zimbabwe (capital Harare ) -
 Somalia (capital Mogadishu )
Somalia (capital Mogadishu ) -
 South Sudan (capital Juba )
South Sudan (capital Juba ) -
 Tanzania (capital Dodoma / seat of government Dar es Salaam )
Tanzania (capital Dodoma / seat of government Dar es Salaam ) -
 Uganda (capital Kampala )
Uganda (capital Kampala )
In addition, the geographical areas British Indian Ocean Territory and French Southern and Antarctic Territories (partially) belong to East Africa.
![]()
![]()
East African Community
The East African Community is a form of economic integration of the East African countries Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda and Burundi with the aim of an economic and customs union.
history
Colonial history
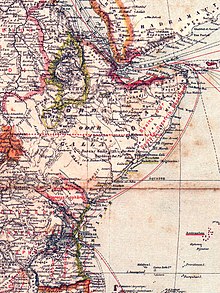
The present-day states of Tanzania (mainland without Zanzibar ), Rwanda and Burundi as well as a small part of Mozambique ( Kionga triangle ) formed the former colony of German East Africa . Kenya was referred to as British East Africa , Mozambique as Portuguese East Africa . Between 1885 and 1890, German representatives tried to establish a hegemony of the German Empire that was to extend from the Somali coast via Wituland to German East Africa. However, the plans failed because of British and Italian colonial efforts. Ethiopia , Eritrea , and Somalia were combined to form Italian East Africa in 1936–1941 , with Ethiopia only being occupied and not all parts being brought under Italian control.
The borders of many states were arbitrarily determined by the colonial powers without regard to cultural or national borders .
1967 Kenya, Tanzania and Uganda formed the East African Community ( East African Community , EAC) economic integration and promoted the spread in all three countries Swahili as East African lingua franca, but in 1977 this community was broken by their opposites and mutual interference. The community was officially re-established in July 2000 and since July 2007 has also included Burundi and Rwanda among its members.
History of tourism
Tourism has a very long tradition in East Africa . The first tourists came at the beginning of the 20th century and were rich people from Europe and America who went on big game hunting . In this early phase, there were also celebrities such as Winston Churchill and the US President Theodore Roosevelt , who needed 500 porters for, among other things, huge amounts of champagne. Big game hunting became popular in the 1920s and 1930s, and writers like Ernest Hemingway immortalized these adventures in their stories, which were often made into films. Big game hunting remained exclusive until the 1960s, although there was already a well-developed hotel and lodge network.
The mass tourism began in the late 1960s. The number of foreign visitors in Kenya rose from 110,000 to 400,000 between 1963 and 1971 . In the 1970s, big game hunting was banned and replaced by "hunting with a camera". Most of the safaris to the Tanzanian attractions Serengeti and Ngorongoro did not start from Tanzania , but from Kenya. When the Kenyan-Tanzanian border was closed in 1977, Tanzania suffered the greatest damage, with visitor numbers falling from 178,000 to 58,000 by 1985. By contrast, Kenya's boom continued, with 540,000 tourists arriving in 1985 (17% more than in the previous year) and almost 650,000 in the following year. The strongest visitor contingents came from Germany (1985 with 100,000), Great Britain , America (60,000) and Switzerland (40,000). In 1988 Kenya had almost 30,000 hotel beds, which means that 80,000 jobs were directly linked to tourism. In 1986, this resulted in income of almost 350 million US dollars, which was the second largest source of foreign currency after coffee.
Broadcast reports
- Linda Staude: Valuable Good - The struggle for scarce drinking water in East Africa , Deutschlandfunk - " Background " from September 1, 2018
- Linda Staude: Family planning as a challenge - East Africa's handling of the population explosion , Deutschlandfunk - "Background" from September 5, 2018
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Standard Country and Area Codes for statistical use (M49). Geographic regions. United Nations Statistics Division, October 31, 2013, accessed December 12, 2013 (ene).
