Terbacil
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
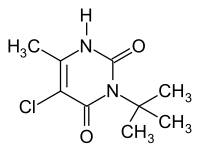
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Terbacil | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 9 H 13 ClN 2 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 216.67 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.34 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
175-177 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Terbacil is a chemical compound from the group of uracil derivatives .
Extraction and presentation
Terbacil can be prepared by chlorination of 3- tert -butyl-6-methyluracil obtained.
properties
Terbacil is a white, flammable solid that is sparingly soluble in water. The compound begins to sublime below its melting point . It is stable to hydrolysis and photolysis in the pH range from 5 to 9.
use
Terbacil is used as a plant protection product. It was first approved as a herbicide in the United States in 1966 and is used to control many annual and perennial weeds.
Admission
Terbacil is not on the list of active ingredients for pesticides permitted in the European Union . In the EU states including Germany and Austria as well as in Switzerland no pesticides with this active substance are permitted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Entry for CAS no. 5902-51-2 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on August 16, 2012(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d EPA: Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) - TERBACIL (PDF; 770 kB), January 1998
- ↑ a b Terbacil data sheet , PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 10, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ^ Entry on Terbacil in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on August 16, 2012.
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 570 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ SD Gangolli: The Dictionary of Substances and their Effects (DOSE) . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-838-3 , pp. 35 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Terry R Roberts, David H Hutson, Philip W Lee, Peter H Nicholls: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Part 1: Herbicides and Plant Growth ... Royal Society of Chemistry, 1998, ISBN 0-85404-494-9 , pp. 702 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 (PDF) of the Commission of November 20, 2002.
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Terbacil in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 8, 2016.

