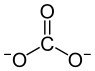
Thallium (I) carbonate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Thallium (I) carbonate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Tl 2 CO 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 468.78 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
7.11 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Thallium (I) carbonate is an inorganic chemical compound of thallium from the group of carbonates .
Extraction and presentation
Thallium (I) carbonate can be obtained by reacting a hot thallium (I) hydroxide solution with carbon dioxide .
properties
Thallium (I) carbonate is a colorless solid that is in the form of needle-shaped crystals with a sharp enantiotropic transformation point at 228 ° C and is soluble in water. It is the only heavy metal carbonate that is readily soluble in water. It is not hygroscopic and can be kept in air up to 175 ° C without noticeable change. Its aqueous solutions react strongly basic as a result of hydrolysis . It melts into a dark gray mass. The connection has a monoclinic crystal structure with the space group C 2 / m (space group no. 12) . At very high pressures, however, this is destroyed.
use
Thallium (I) carbonate can be used to make artificial diamonds and to test for carbon disulfide .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Georg Brauer , with the assistance of Marianne Baudler u. a. (Ed.): Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry . 3rd, revised edition. tape I . Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , pp. 887 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet Thallium (I) carbonate, ≥99.99% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 6, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Erwin Riedel, Christoph Janiak: Inorganic Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 2011, ISBN 3-11-022566-2 , p. 615 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b Dale L. Perry: Handbook of Inorganic Compounds . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 0-8493-8671-3 , pp. 406 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ A. Grzechnik, K. Friese: Crystal structure and stability of Tl2CO3 at high pressures. In: Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 66, 2010, pp. I37-i38, doi : 10.1107 / S0108270110005652 .
- ^ Robert E. Krebs: The History and Use of Our Earth's Chemical Elements: A Reference Guide . Greenwood Publishing Group, 2006, ISBN 0-313-33438-2 , pp. 188 ( limited preview in Google Book search).



