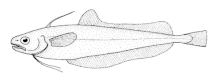
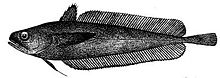
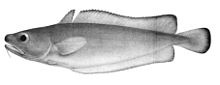
Deep sea cod
| Deep sea cod | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Moridae | ||||||||||||
| Moreau , 1881 |
The deep-sea cod (Moridae) form a family within the order of the cod-like (Gadiformes). They live mostly pelagic in all oceans on the continental slopes and in the deep sea at depths of up to 2500 meters.
features
Deep-sea cod have a slim body, covered with small round scales , which ends in a thin tail stalk. They have one or two, rarely three dorsal fins, and one or two anal fins. The dorsal, anus and caudal fin are separate. The pelvic fins are on the chest. They are usually dark in color, often with silvery spots.
The mouth is terminal or below, the gap between the mouths is deep, but does not reach under the eyes. The gill opening is wide. The goatee typical of cod-like species is only present in some species. The tip of the vomer is toothless; the genus Mora has only very small teeth. The swim bladder is in contact with the ear through a pair of front bulges. Some species have luminous organs . Deep sea cod have 41 to 72 vertebrae .
Systematics
There are about 110 species in 18 genera:
-
Antimora
- Antimora microlepis Bean , 1890 .
- Antimora rostrata ( Günther , 1878) .
-
Auchenoceros
- Auchenoceros punctatus (Hutton, 1873) .
-
Eeyorius
- Eeyorius hutchinsi Paulin, 1986 .
-
Eretmophorus
- Eretmophorus kleinebergi Giglioli , 1889 .
-
Gadella
- Gadella brocca Paulin & Roberts, 1997 .
- Gadella dancoheni Sazonov & Shcherbachev, 2000 .
- Gadella edelmanni ( brewer , 1906) .
- Gadella filifer ( Garman , 1899) .
- Gadella imberbis ( Vaillant , 1888) .
- Gadella jordani (Böhlke & Mead, 1951) .
- Gadella macrura Sazonov & Shcherbachev, 2000 .
- Gadella maraldi ( Risso , 1810) .
- Gadella molokaiensis Paulin, 1989 .
- Gadella norops Paulin, 1987 .
- Gadella obscurus (Parin, 1984) .
- Gadella svetovidovi Trunov, 1992 .
- Gadella thysthlon Long & McCosker, 1998 .
-
Guttigadus
- Guttigadus globiceps (Gilchrist, 1906) .
- Guttigadus globosus (Paulin, 1986) .
- Guttigadus kongi (Markle & Meléndez C., 1988) .
- Guttigadus latifrons (Holt & Byrne, 1908) .
- Guttigadus nudicephalus (Trunov, 1990) .
- Guttigadus nudirostre (Trunov, 1990) .
- Guttigadus squamirostre (Trunov, 1990) .
-
Halargyreus
- Halargyreus johnsonii Günther, 1862 .
-
Laemonema
- Laemonema barbatulum Goode & Bean , 1883 .
- Laemonema compressicauda (Gilchrist, 1903) .
- Laemonema filodorsale Okamura, 1982 .
- Laemonema goodebeanorum Meléndez C. & Markle, 1997 .
- Laemonema gracillipes Garman , 1899 .
- Laemonema laureysi Poll, 1953 .
- Laemonema longipes Schmidt, 1938 .
- Laemonema macronema Meléndez C. & Markle, 1997 .
- Laemonema melanurum Goode & Bean, 1896 .
- Laemonema modestum (Franz, 1910) .
- Laemonema nana Taki, 1953 .
- Laemonema palauense Okamura, 1982 .
- Laemonema rhodochir Gilbert, 1905 .
- Laemonema robustum Johnson, 1862 .
- Laemonema verecundum ( Jordan & Cramer, 1897) .
- Laemonema yarrellii (Lowe, 1838) .
- Laemonema yuvto Parin & Sazonov, 1990 .
-
Lepidion
- Lepidion capensis Gilchrist, 1922 .
- Lepidion ensiferus ( Günther , 1887) .
- Lepidion eques (Günther, 1887) .
- Lepidion guentheri ( Giglioli , 1880) .
- Lepidion inosimae (Günther, 1887) .
- Lepidion lepidion ( Risso , 1810) .
- Lepidion microcephalus Cowper, 1956 .
- Lepidion natalensis Gilchrist, 1922 .
- Lepidion schmidti Svetovidov, 1936 .
-
Lotella
- Lotella fernandeziana Rendahl , 1921 .
- Lotella fuliginosa Günther, 1862 .
- Lotella phycis ( Temminck & Schlegel , 1846) .
- Lotella rhacina ( Forster , 1801) .
- Lotella schuettei Steindachner , 1866 .
- Lotella tosaensis (Kamohara, 1936) .
- Mora
-
Notophycis
- Notophycis fitchi Sazonov, 2001 .
- Notophycis marginata (Günther, 1878) .
-
Physiculus
- Physiculus andriashevi Shcherbachev, 1993 .
- Physiculus argyropastus Alcock , 1894 .
- Physiculus beckeri Shcherbachev, 1993 .
- Physiculus bertelseni Shcherbachev, 1993 .
- Physiculus caboverdensis Gonzáles et al., 2018 .
- Physiculus capensis (Gilchrist, 1922) .
- Physiculus chigodarana Paulin, 1989 .
- Physiculus coheni Paulin, 1989 .
- Physiculus cyanostrophus Anderson & Tweddle, 2002 .
- Physiculus cynodon Sazonov, 1987 .
- Physiculus dalwigki Kaup , 1858 .
- Physiculus fedorovi Shcherbachev, 1993 .
- Physiculus fulvus Bean , 1884 .
- Physiculus grinnelli Jordan & Jordan , 1922 .
- Physiculus helenaensis Paulin, 1989 .
- Physiculus hexacytus Parin, 1984 .
- Physiculus huloti Poll, 1953 .
- Physiculus japonicus Hilgendorf, 1879 .
- Physiculus karrerae Paulin, 1989 .
- Physiculus kaupi Poey , 1865 .
- Physiculus longicavis Parin, 1984 .
- Physiculus longifilis Weber, 1913 .
- Physiculus luminosus Paulin, 1983 .
- Physiculus marisrubri Brüss, 1986 .
- Physiculus maslowskii Trunov, 1991 .
- Physiculus microbarbata Paulin & Matallanas, 1990 .
- Physiculus natalensis (Gilchrist, 1922) .
- Physiculus nematopus Gilbert, 1890 .
- Physiculus nielseni Shcherbachev, 1993 .
- Physiculus nigripinnis Okamura, 1982 .
- Physiculus nigriscens Smith & Radcliffe, 1912 .
- Physiculus normani Brüss, 1986 .
- Physiculus parini Paulin, 1991 .
- Physiculus peregrinus (Günther, 1872) .
- Physiculus Rastrelliger Gilbert, 1890 .
- Physiculus rhodopinnis Okamura, 1982 .
- Physiculus roseus Alcock , 1891 .
- Physiculus sazonovi Paulin, 1991 .
- Physiculus sterops Paulin, 1989 .
- Physiculus talarae Hildebrand & Barton, 1949 .
- Physiculus therosideros Paulin, 1987 .
- Physiculus yoshidae Okamura, 1982 .
-
Pseudophycis
- Pseudophycis bachus ( Forster , 1801) .
- Pseudophycis barbata Günther, 1863 .
- Pseudophycis breviuscula ( Richardson , 1846) .
-
Rhynchogadus
- Rhynchogadus hepaticus (Facciolà, 1884) .
-
Salilota
- Salilota australis (Barnard, 1925) .
-
Svetovidovia
- Svetovidovia lucullus (Jensen, 1953) .
-
Tripterophycis
- Tripterophycis gilchristi Boulenger , 1902 .
- Tripterophycis svetovidovi (Trunov, 1992) .
literature
- Joseph S. Nelson : Fishes of the World , John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7
- Kurt Fiedler: Textbook of Special Zoology, Volume II, Part 2: Fish . Gustav Fischer Verlag Jena, 1991, ISBN 3-334-00339-6
Web links
- Deep sea cod on Fishbase.org (English)