Trögersche Base
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
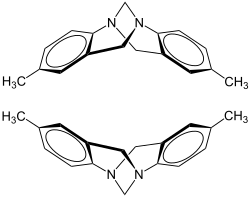
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (5 S , 11 S ) - (-) - shape (top) and (5 R , 11 R ) - (+) - shape (bottom) | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Trögersche Base | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 18 N 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 250.34 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
133-136 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
The Tröger's base is after its discoverer, the chemist Julius Tröger (1862-1942), named heterocyclic compound corresponding to the organic is attributed chemistry.
structure
Tröger's base contains two pyramidal nitrogen atoms that form stereocenters. As a rule, the inversion of pyramidal nitrogen atoms with three different radicals (and a lone pair of electrons) proceeds very quickly, so that such substances racemize quickly - not so with Tröger's base. In Tröger's base, both nitrogen atoms are in a bridgehead position, making a pyramidal inversion impossible. There are therefore two stable enantiomers of Tröger's base that can be separated, for example, by chromatography on a chiral stationary phase.
Manufacturing
Tröger's base was first synthesized in 1887 from p -toluidine and formaldehyde in acidic solution. The correct structural formula was not determined until 1935. Tröger's base can also be prepared from p -toluidine, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and hydrochloric acid or p -toluidine and urotropine (hexamethylenetetramine). All these synthetic methods lead to the racemate of Tröger's base.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Trögersche Base at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 11, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd Edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, p. 96, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 .
- ^ Ernest L. Eliel, Samuel H. Wilen: Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds , John Wiles & Sons, 1994, p. 360, ISBN 0-471-05446-1 .
- ↑ Julius Tröger: About some bases formed by means of nascent formaldehyde. In: Journal for Practical Chemistry . 36, 1887, pp. 225-245, doi : 10.1002 / prac.18870360123 .
- ^ MA Spielman: The Structure of Troeger's Base. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society 57, 1935, pp. 583-585, doi : 10.1021 / ja01306a060 .
- ↑ Zhong Li, Xiaoyong Xu, Yanqing Peng, Zhaoxing Jiang, Chuanyong Ding, Xuhong Qian: An Unusual Synthesis of Troeger's Bases Using DMSO / HCl as Formaldehyde Equivalent. In: Synthesis 2005, pp. 1228-1230, doi : 10.1055 / s-2005-861868 .
- ↑ Thierry Masa, Carmen Pardo, José Elguero: A shorter synthesis of symmetrical 2,11-dimethyl-bis-Tröger's bases. A new molecular tweezer. In: Arkivoc . 2004, (EM-973K).
