Transaldolase
| Transaldolase | ||
|---|---|---|

|
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 337 amino acids | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | TALDO1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.2.1.2 , transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of a CHOH residue | |
| Substrate | Sedoheptulose-7-phosphate + D- glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate | |
| Products | D- erythrose-4-phosphate + D- fructose-6-phosphate | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | Transaldolase | |
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
Transaldolase (TAL) (gene: TALDO1 ) is the name of the enzyme that enables the transfer of a C3 body from sedoheptulose-7-phosphate to D - glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and vice versa. This equilibrium of reactions is an important part of the pentose phosphate pathway in all living things.
Mutations can cause the (rare) hereditary disease transaldolase deficiency .
Catalyzed equilibrium
 |
D - erythrose-4-phosphate | + | 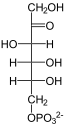 |
D - fructose-6-phosphate |
|
|
||||

|
D - glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate | + |

|
D - Sedoheptulose-7-phosphate |
Physiological effects
The regulation of gene expression in TALDO1 - gene may the glutathione levels and the sensitivity of cells to apoptosis influence.
Diseases
Some multiple sclerosis patients have antibodies against areas of transaldolase.
Transaldolase shortage
Mutations in the TALDO1 gene can lead to the (rare) hereditary disease of transaldolase deficiency and this to liver cirrhosis . Also, multi-organ failure may occur in Transaldolasemangel.
Other genetic defects
Variants of the enzyme may be associated with squamous cell carcinoma .
application
Differentiations of the bacterial transaldolase gene by means of the polymerase chain reaction are used to identify and quantify an intestinal colonization by Bifidobacterium .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Katalin Banki, Eliza Hutter, Emanuela Colombo, Nick J. Gonchoroff, Andras Perl: Glutathione levels and sensitivity to apoptosis are regulated by changes in transaldolase expression. In: Journal of Biological Chemistry . Volume 271, No. 51, 1996, pp. 32994-33001, doi : 10.1074 / jbc.271.51.32994 .
- ↑ Niland B, Banki K, Biddison WE, Perl A: CD8 + T cell-mediated HLA-A * 0201-restricted cytotoxicity to transaldolase peptide 168-176 in patients with multiple sclerosis . In: J. Immunol. . 175, No. 12, December 2005, pp. 8365-8378. PMID 16339578 .
- ↑ Nanda M. Verhoeven, Jojanneke HJ Huck, Birthe Roos, Eduard A. Struys, Gajja S. Salomons, Adriaan C. Douwes, Marjo S. van der Knaap, Cornelis Jakobs: Transaldolase deficiency: liver cirrhosis associated with a new inborn error in the pentose phosphate pathway. In: The American Journal of Human Genetics . Volume 68, No. 5, 2001, pp. 1086-1092, doi : 10.1086 / 320108 .
- ↑ Vassili Valayannopoulos, Nanda M. Verhoeven, Karine Mention, Gajja S. Salomons, Danièle Sommelet, Marie Gonzales, Guy Touati, Pascale de Lonlay, Cornelis Jakobs, Jean-Marie Saudubray: Transaldolase deficiency: a new cause of hydrops fetalis and neonatal multi -organ disease. In: The Journal of Pediatrics . Volume 149, No. 5, 2006, pp. 713-717, doi : 10.1016 / j.jpeds.2006.08.016 .
- ↑ UniProt P37837
- ↑ Qian Y, Banerjee S, Grossman CE, et al : Transaldolase deficiency influences the pentose phosphate pathway, mitochondrial homoeostasis and apoptosis signal processing . In: Biochem. J. . 415, No. 1, October 2008, pp. 123-34. doi : 10.1042 / BJ20080722 . PMID 18498245 .
- ↑ Basta PV, Bensen JT, Tse CK, Perou CM, Sullivan PF, Olshan AF: Genetic variation in Transaldolase 1 and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck . In: Cancer Detect. Prev. . 32, No. 3, 2008, pp. 200-208. doi : 10.1016 / j.cdp.2008.08.008 . PMID 18805652 .
- ↑ Teresa Requena, Jeremy Burton, Takahiro Matsuki, Karen Munro, Mary Alice Simon, Ryuichiro Tanaka, Koichi Watanabe, Gerald W. Tannock: Identification, detection, and enumeration of human Bifidobacterium species by PCR targeting the transaldolase gene. In: Applied and Environmental Microbiology . Volume 68, No. 5, 2002, pp. 2420-2427, doi : 10.1128 / AEM.68.5.2420-2427.2002 .