Trimethyl tin chloride
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
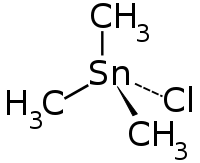
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Trimethyl tin chloride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 9 ClSn | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
White |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 199.27 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
solid, crystalline |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.65 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
37-39 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
154 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
2.5 hPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water: 93.3 g l −1 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
0.001 ml m −3 , 0.005 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Trimethyltin chloride is a chemical compound from the group of organotin compounds .
Extraction and presentation
Trimethyltin chloride can be produced by reacting tetramethyltin with hydrogen chloride :
properties
Physical Properties
Trimethyl tin chloride is a white, flammable solid with a flash point of 97 ° C that slowly decomposes in water. In benzene it has a dipole moment of 3.46 Debye .
Chemical properties / use
Since the chloride ligand is very reactive and can easily be replaced, trimethyltin chloride is a starting material for the production of other trimethyltin compounds. By reducing trimethyltin chloride with a suitable reducing agent (e.g. lithium aluminum hydride ), trimethyltin hydride can be obtained:
The reaction with lithium alkyls yields the corresponding trimethylalkyltin with the formation of lithium chloride:
Safety instructions / toxicity
Trimethyltin chloride, like many other organic tin compounds, is classified as toxic and must therefore be handled with appropriate care. The toxic effect is particularly targeted on the kidneys and the central nervous system , and in higher doses also on the liver , adrenal glands , thymus , spleen , urinary bladder , testes and epididymis .
- Toxicity to fish: LC 50 Oryzias latipes (48 h ) 5.62 mg l −1
- Toxicity to aquatic invertebrates: EC 50 Daphnia magna (24 h) 0.47 mg · l −1
- Toxicity to algae: Growth inhibition EC 50 Skeletonema costatum (72 h) 0.214 mg · l −1
- Toxicity to mammals: LD 50 oral, rat 1.26 mg kg −1
- Bioaccumulative potential: Cyprinodon sp. (Kärpfling) (45 d) 10 μg l −1
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h data sheet Trimethyltin chloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 1, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d methyl tin compounds . In: DFG (Ed.): The MAK Collection for Occupational Health and Safety . 2014, p. 13 , doi : 10.1002 / 3527600418.mb744031metd0056 .
- ↑ a b c d e f Entry on trimethyltin chloride in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c Didier Astruc: Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis. Springer Science & Business Media, 2007, ISBN 978-3-540-46129-6 , p. 336 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Jörg Lorberth, Heinrich Nöth: Dipole moments of some organotin chlorides . In: Chemical Reports . tape 98 , no. 3 , March 1965, p. 969-976 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19650980342 .


![{\ mathrm {Sn (CH_ {3}) _ {4} \ + \ HCl \ quad {\ xrightarrow [{}] {}} \ ClSn (CH_ {3}) _ {3} + \ CH_ {4}} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a2d13757ea0196466a8f26e61b327b154086a8ad)

