Tris (dimethylamino) methane
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tris (dimethylamino) methane | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 19 N 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Clear colorless to pale yellow liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 145.25 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.838 g cm −3 at 20 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
42-43 ° C at 16 hPa |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
miscible with non-polar, aprotic, anhydrous solvents |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4360 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Tris (dimethylamino) methane ( TDAM ) is the simplest representative of tris (dialkylamino) methanes of the general formula (R 2 N) 3 CH, in which three of the four hydrogen atoms of methane have been replaced by dimethylamino groups (-N (CH 3 ) 2 ) . Tris (dimethylamino) methane can be understood as both an amine and an ortho-amide .
TDAM is a strong base and can be used as a formylating agent, as a reagent for aminomethylenation and as a source of the basic carbene bis (dimethylamino) carbene of the formula R 2 N-C: -NR 2 .
Occurrence and representation
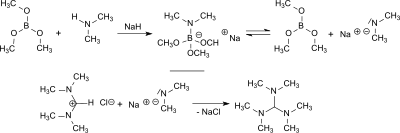
Tris (dimethylamino) methane is formed in the reaction of N , N , N ', N ' -tetramethylformamidinium chloride or bis (dimethylamino) acetonitrile with lithium dimethylamide or sodium dimethylamide with yields between 55 and 84%.
From dimethylamine and sodium hydride , in the presence of trimethyl borate, sodium dimethylamide is formed in situ , which forms TDAM with N , N , N ', N ' -tetramethylformamidinium chloride in 84% yield and with bis (dimethylamino) acetonitrile in 77% yield.
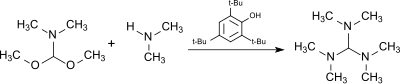
The reaction of dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal (from DMF dimethyl sulfate complex and sodium methoxide ) with dimethylamine in the presence of the acidic catalyst 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenol, which is largely stable to alkylating agents, produces tris (dimethylamino) methane.
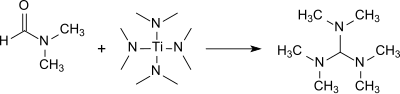
TDAM is formed in good yield (83%) when DMF reacts with tetrakis (dimethylamino) titanium .
Of N , N , N ', N ', N '', N '' -Hexamethylguanidiniumchlorid (about from tetramethylurea and phosgene resulting N , N , N ', N available' -tetramethyl-chloroformamidinium chloride and dimethylamine simply) is formed under Action of the reducing agent sodium bis (2-methoxyethoxy) aluminum hydride ( Red-Al ) tris (dimethylamino) methane in 53% yield.
Sodium hydride and trimethyl borate reduce N , N , N ', N ', N '', N '' -hexamethylguanidinium chloride in 80% yield to TDAM.
properties
Tris (dimethylamino) methane is a clear, colorless or slightly yellow colored liquid with a strong amine-like odor. The compound can be mixed with many non-polar aprotic and anhydrous solvents. TDAM reacts with protic solvents such as water and alcohols, but also with weakly CH-acidic substances such as acetone or acetonitrile when heated.
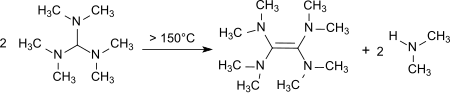
When heated to temperatures of 150–190 ° C, decomposition occurs with formation of tetrakis (dimethylamino) ethene,
a strong electron donor .
Applications
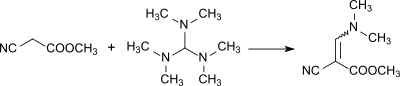
Tris (dimethylamino) methane dissociates into N , N , N ′, N ′ -tetramethylformamidinium cations and dimethylamide anions, which abstract protons from CH- and NH-acidic compounds. The anions thus formed add to the formamidinium cations with the formation of adducts, which in turn eliminate dimethylamine and react in the sense of aminomethylenation to dimethylaminomethylene (= CH-N (CH 3 ) 2 compounds) or to form amidines.
Reaction to dimethylaminomethylene:
Reaction to amidines:
The aminomethylenation provides intermediates for the synthesis of heterocycles , such as. B. pyrimidines , pyrazoles , 1,4-dihydropyridines and indoles .
Long heating of TDAM with selenium in xylene makes N , N , N ′, N ′ -tetramethylselenourea accessible, bis (dimethylamino) carbene being assumed to be an intermediate.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Tris (dimethylamino) methane from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 4, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on tris (dimethylamino) methane at TCI Europe, accessed on December 10, 2016.
- ↑ a b c d e W. Kantlehner: Tris (dimethylamino) methane . In: e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . 2001, doi : 10.1002 / 047084289X.rt403 .
- ^ A b H. Bredereck, F. Effenberger, T. Brendle: Synthesis and reactions of trisdimethylaminomethane . In: Angew. Chem. Band 78 , no. 2 , 1966, p. 147-148 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19660780212 .
- ↑ Patent DE1217391 : Process for the production of tris-dimethylaminomethane. Applied on September 29, 1964 , published on December 8, 1966 , applicant: H. Bredereck, inventor: H. Bredereck, F. Effenberger, T. Brendle.
- ↑ H. Bredereck, F. Effenberger, T. Brendle, H. Muffler: Orthoamide, V. Synthesis of Tris-dialkylamino-methanes . In: Chem. Ber. tape 101 , no. 5 , 1968, p. 1885–1888 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.19681010541 .
- ↑ W. Kantlehner, T. Maier, P. Speh: Tris [dialkylamino] methane and tetraalkylformamidinium thiocyanate from bis [dialkylamino] acetonitriles . In: Synthesis . tape 5 , 1979, pp. 342-343 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1979-28671 .
- ↑ a b W. Kantlehner, R. Stieglitz, M. Hauber, E. Haug, C. Regele: Orthoamide. LII Contributions to the Synthesis of Orthocarboxamides . In: J. Prakt. Chem. Volume 342 , no. 3 , 2000, pp. 256-268 , doi : 10.1002 / (SICI) 1521-3897 (200003) 342: 3 <256 :: AID-PRAC256> 3.0.CO; 2-G .
- ↑ H. Bredereck, F. Effenberger, G. Simchen: Reactive acid amide dimethyl sulfate complexes . In: Angew. Chem. Band 73 , no. 14 , 1961, pp. 493 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19610731407 .
- ↑ Patent DE2214497 : Process for the production of an amino-substituted methane derivative. Registered on March 24, 1972 , published October 5, 1972 , applicant: F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co. AG, inventor: W. Leimgruber, AE Wick.
- ↑ H. Weingarten, WA White: A novel amination reaction of carboxylic acid derivatives with tetrakis (dimethylamino) titanium . In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. tape 88 , no. 4 , 1966, pp. 850-850 , doi : 10.1021 / ja00956a049 .
- ↑ W. Kantlehner, E. Haug, WW Mergen, P. Speh, T. Maier, JJ Kapassakalidis, HJ Bräuner, H. Hagen: A manufacturing process for N, N, N ′, N ′, N ′ ′, N ′ ′ -Hexaalkylguanidinium chloride . In: Synthesis . tape 11 , 1983, pp. 904-905 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1983-30558 .
- ↑ W. Kantlehner, P. Speh, HJ Bräuner: A simple synthesis for tris [dialkylamino] methane . In: Synthesis . tape 11 , 1983, pp. 905 , doi : 10.1055 / s-1983-30559 .
- ↑ H. Bredereck, F. Effenberger, HJ Bredereck: A new synthesis of tetra- (dimethylamino) -ethylene . In: Angew. Chem. Band 78 , no. 21 , 1966, pp. 984 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19660782113 .
- ^ N. Wiberg, JW Buchler: Tetrakis (dimethylamino) ethylene: a strong electron donor . In: Angew. Chem. Band 74 , no. 14 , 1962, pp. 490-491 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19620741410 .
- ↑ H. Bredereck, F. Effenberger, T. Brendle: Synthesis and reactions of Trisdimethylaminomethan . In: Angew. Chem. Band 78 , no. 2 , 1966, p. 147-148 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19660780212 .
- ↑ W. Lehner Kant, M. Hauber, M. Vettel: Orthoamide.IL. Reactions of orthoamide derivatives with sulfur and selenium, syntheses of 1,3-thiazole and 1,3-selenazole derivatives . In: J. Prakt. Chem. Volume 338 , no. 1 , 1996, p. 403-413 , doi : 10.1002 / prac.19963380180 .