Submarine class R
| R-class |
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| General data | ||
| Ship type : | ||
| Navy : | ||
| Builders : |
|
|
| Units: |
|
|
| Boats of the class | ||
|
|
||
| Technical specifications | ||
| Crew: |
|
|
| Displacement : |
|
|
| Length : |
|
|
| Width: |
|
|
| Draft : |
|
|
| Drive : |
|
|
| Speed : | ||
| Driving range: |
|
|
| Diving depth : | ||
| Armament | ||
| Torpedo tubes : |
|
|
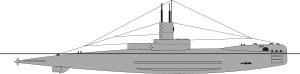
The R-Class was a class of British Royal Navy submarines that was designed and built during World War I. The intended mission was to hunt down enemy submarines , which is why the submarine type had a number of extremely advanced features.
history
Development began in the fall of 1916, and the first units were laid down in February 1917 and entered service during 1918. The boats were to operate from Killybegs in Donegal . One of the R-class boats attacked a German submarine in October 1918 with a full volley of six torpedoes, but all of them failed or did not detonate.
After the end of the war, there was no longer any need for the submarines, so the construction of two as yet unfinished submarines was stopped and the rest of them, except for the R4 and R10, were gradually decommissioned and canceled until 1923. The R4 and R10 were then used for anti-submarine training on the Isle of Portland , with the R10 being sold in 1929, while the R4 was used for targeting until 1934.
construction
The concept for using the R-Class for submarine hunting was to track down and attack enemy submarines while submerged. Therefore, the entire construction of this type was geared towards this particular tactic. The hull was streamlined and dispensed with flow resistances such as a deck gun or external tanks. The machine system was also designed for underwater travel and, in addition to the diesel engine for surface travel, consisted of two coupled electric motors that acted together on a single propeller shaft. For the class also the consisting of 200 cells battery of the J-Class over who could only provide power for an hour drive but under full load. Since the charging process at sea could take up to a day and required half the power of the diesel engine, the R-class batteries were mostly precharged in port.
The construction measures taken for the underwater mileage resulted in a record speed of 14 kn (27.6 km / h) at the time, but the submarines proved difficult to control at high speeds. Likewise, the submarines were slow and not very seaworthy when sailing on the surface. R4 was later modified, which improved the driving characteristics, but reduced the underwater speed to 13 kn (24 km / h).
As a further technological novelty, the R-Class was equipped with five hydrophones , which were housed in the arched bow and with which the submarines to be attacked were to be tracked during submerged voyage. The armament consisted of six torpedo tubes of caliber 457 mm. This also shows the use of lighter torpedoes against underwater targets, which is still common today, while heavier torpedoes of calibers such as 533 mm or 650 mm are usually used for surface targets.
Units of class
| boat | Shipyard | Keel laying | Launch | Commissioning | comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMS R1 | Chatham Dockyard | February 4, 1917 | April 25, 1918 | October 14, 1918 | Sold in 1923 |
| HMS R2 | Chatham Dockyard | February 4, 1917 | December 20, 1918 | Sold in 1923 | |
| HMS R3 | Chatham Dockyard | February 4, 1917 | June 8, 1918 | March 17, 1919 | Sold in 1923 |
| HMS R4 | Chatham Dockyard | March 4, 1917 | June 8, 1918 | August 23, 1919 | modified and used for anti-submarine training, sold in 1934 |
| HMS R5 | Pembroke Dock | March 1918 | Construction stopped on August 28, 1919 | ||
| HMS R6 | Pembroke Dock | March 1918 | Construction stopped on August 28, 1919 | ||
| HMS R7 | Vickers | November 1, 1917 | May 14, 1918 | June 29, 1918 | Stationed in Donegal in November 1918, sold in 1923 |
| HMS R8 | Vickers | November 1, 1917 | June 28, 1918 | July 25, 1918 | Stationed in Donegal in November 1918, sold in 1923 |
| HMS R9 | Armstrong Whitworth | December 1, 1917 | August 12, 1918 | July 26, 1919 | Sold in 1923 |
| HMS R10 | Armstrong Whitworth | December 7, 1917 | October 5, 1918 | April 12, 1919 | Further used for anti-submarine training, sold in 1929 |
| HMS R11 | Cammell Laird | December 1, 1917 | March 16, 1918 | August 8, 1919 | Sold in 1923 |
| HMS R12 | Cammell Laird | December 1, 1917 | April 9, 1918 | October 29, 1919 | Sold in 1923 |
See also
Web links
- K-class at www.battleships-cruisers.co.uk ( engl. )
- U-boat database at www.submariners.co.uk (English)
literature
- Robert Hutchinson: KAMPF UNDER WASSER - Submarines from 1776 to today , Motorbuchverlag, Stuttgart, 1st edition 2006, ISBN 3-613-02585-X
- Anthony Preston: The history of the submarines , Karl Müller Verlag, Erlangen, German edition 1998, ISBN 3-86070-697-7

