deformation
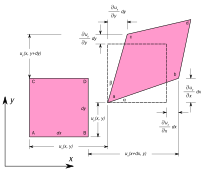
In continuum mechanics, deformation (also called deformation or distortion ) of a body is the change in its shape due to the action of an external force . The deformation can be used as change in length ( elongation ) or as an angular change ( shear ) appear. The deformation is represented using the strain tensor . The force of the body opposing the external force is the deformation resistance .
separations
Deformations can be broken down into:
- an isotropic part (isotropic change in size while maintaining the shape) and
- a deviatoric part (change of shape while maintaining volume).
In addition, deformations consist of
- elastic ( reversible ) components and
- plastic ( irreversible ) components.
Furthermore, deformations are divided into
- spontaneous deformations and
- viscous deformations.
Reversible elastic deformation
A reversible - i.e. a reversible or non-permanent - deformation is called elastic deformation . The associated material property is called elasticity .
Irreversible plastic deformation
An irreversible, i.e. permanent, deformation once a flow limit has been reached is called plastic deformation . This requires that a material formability is; the associated property of a material is called plasticity .
The irreversible deformation of materials without a flow limit (e.g. most liquids) is called viscous deformation .
If the material is very brittle, it breaks without any relevant deformation beforehand. With rocks , this is the case with displacements in the millimeter to centimeter range per year, while slower processes take place plastically (see fold (geology) , tectonics ).
Primary plastic deformation can also be completely reversible on the nanoscale. This assumes that no material transport in the form of transverse sliding has yet started.
See also
- The deformation of elongated bodies such as beams or rods when subjected to bending loads is known as deflection .
- Mechanics of solid bodies , law of matter
- Rigid body - the idealization of a body without deformation
- Deformation energy , earth flattening
- Tension (mechanics) , breaking load
- Pressure , bending strength , heat resistance
- The rolling resistance depends on the deformation of the bodies involved.
- Cold forming , forming processes
Individual evidence
- ^ Gerolf Ziegenhain, Herbert M. Urbassek: Reversible Plasticity in fcc metals. In: Philosophical Magazine Letters. 89 (11): 717-723, 2009, doi : 10.1080 / 09500830903272900 .

