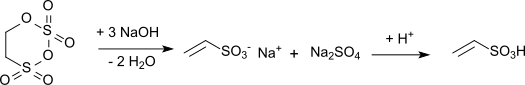Vinyl sulfonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Vinyl sulfonic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Ethylene sulfonic acid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 4 O 3 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid that quickly turns yellow-brown in air |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 108.12 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.392 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4499 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Vinyl sulfonic acid is the simplest representative of unsaturated sulfonic acids . The activated double bond causes the high reactivity towards nucleophilic agents and the pronounced tendency to polymerize, especially when used as a comonomer with functional vinyl and (meth) acrylic acid compounds.
Extraction and presentation
Vinyl sulfonic acid can be made by dehydrating isethionic acid using phosphorus pentoxide :
The sulfochlorination of chloroethane according to Reed, dehydrohalogenation to vinyl sulfonyl chloride and subsequent hydrolysis of the acid chloride also leads to vinyl sulfonic acid.
Only the alkaline hydrolysis of carbyl sulfate with subsequent acidification of the resulting sodium vinyl sulfonate is technically relevant :
The reaction is strongly exothermic with a reaction enthalpy of 1,675 kJ / kg and requires the exact adherence to temperature and pH value during the hydrolysis . With calcium hydroxide as the hydrolysis medium, a solution of calcium vinyl sulfonate results, from which when acidified with conc. Sulfuric acid precipitates poorly soluble calcium sulfate and a colorless vinyl sulfonate solution is obtained.
properties
Pure vinyl sulfonic acid is a colorless, viscous and water-attracting liquid that quickly turns yellow-brown to dark red in air. Cleaning by decolorization with activated carbon and vacuum distillation, as well as stabilization of the oxidation-sensitive substance, e.g. B. MEHQ require considerable effort, but are essential to achieve high molecular weights in (co) polymerization or when used in electronic materials. Aqueous vinylsulfonic acid solutions are very acidic.
use
Nucleophiles can easily be added to the activated double bond of vinyl sulfonic acid; This creates taurine with ammonia and N-methyltaurine with methylamine , which is used as the starting material for the surfactant class of taurides . Vinyl sulfonic acid is used as a reactive monomer for the production of strongly acidic or anionic homo- and copolymers, which are used in the electronics industry in photoresists , as conductive polymers and in polymer electrolyte membranes (PEM) for fuel cells . Polyvinyl sulfonic acid forms transparent membranes with high ion exchange capacity and proton conductivity. Vinyl sulfonic acid can also be applied to polymeric carriers, such as. B. polystyrene can be grafted, with strongly acidic ion exchangers are obtained, which are suitable as catalysts for esterifications and Friedel-Crafts acylations . Where the sulfonic acid functionality is not absolutely necessary, the much more user-friendly alkaline-aqueous solution of sodium vinyl sulfonate , which is obtained directly from the alkaline hydrolysis of the carbyl sulfate, is used.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Patent US3872165 : Manufacture of vinyl sulfonates and vinyl sulfonic acid from carbyl sulfate. Registered on November 30, 1971 , published on March 18, 1975 , applicant: BASF , inventor: Roland Dahlinger, Walter Schenk, Dieter Stockburger.
- ↑ Entry on vinyl sulfonic acid at ChemBlink , accessed on August 6, 2012.
- ↑ Entry on vinyl sulfonic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on May 26, 2014.
- ^ HC Haas, MS Simon: Reactivity ratios of some monomer pairs in J. Polymer Sci. 9 (1952) 309-314, doi : 10.1002 / pol . 1952.120090403 .
- ↑ Le Berre et al .: Bulletin de la Societe Chimique de France 1970, 954-957.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ H. Distler: On the chemistry of vinyl sulfonic acid in Angew. Chem. 77 (1965) 291-311, doi : 10.1002 / anie.19650770704 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Patent EP0643081 : Polymers of vinyl sulfonic acid. Published on March 15, 1995 , Applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor H. Hoffmann et al ..
- ↑ Patent US2011017954 : VINYL SULFONIC ACID, POLYMER THEREOF, AND PRODUCTION METHOD THEREOF. Published on January 27, 2011 , inventor H. Akikaze et al ..
- ↑ Patent US2597696 : Preparation of ethylenesulfonic acid. Applied on March 18, 1948 , published May 20, 1952 , applicant: American Cyanamid , inventor: JA Anthes, JR Dudley.
- ↑ a b Patent US3312735 : Purification of ethylenesulfonic acid. Filed September 30, 1963 , published April 4, 1967 , Applicant: Dow Chemical , Inventor: Robert C. Medford, Charles R. Pfeifer.
- ↑ Patent EP2128131 : PROCESS FOR PRODUCING VINYLSULFONIC ACID. Published on December 2, 2009 , Applicant: Asahi Kasei Finechem Co. Ltd., Inventor: H. Akikaze et al ..
- ↑ Teruyuki Okayasu, Toshiyasu Hibino, Hiroyuki Nishide: Free Radical Polymerization Kinetics of Vinylsulfonic Acid and Highly Acidic Properties of its Polymer . In: Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics . tape 212 , no. 10 , May 17, 2011, p. 1072-1079 , doi : 10.1002 / macp.201000773 ( PDF ).
- ^ T. Okayasu, K. Saito, H. Nishide, MT W. Hearn: Poly (vinylsulfonic acid) -grafted solid catalysts: new materials for acid-catalysed organic synthetic reactions . In: Green Chem . 12 (2010) 1981-1989, doi : 10.1039 / C0GC00241K .