Vismodegib
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
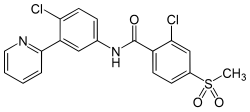
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Vismodegib | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-chloro- N - (4-chloro-3-pyridin-2-ylphenyl) -4-methylsulfonylbenzamide |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 19 H 14 Cl 2 N 2 O 3 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 421.3 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
168-180 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
well soluble in DMSO |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Vismodegib is a medicine that is used in the oral treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma . Vismodegib is the first representative of the new drug class ("first-in-class") of Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors. It was approved in this indication as Erivedge in January 2012 in the USA and in July 2013 in the EU (manufacturer Roche ).
Structure and properties
Vismodegib is a chlorinated methylsulfonylbenzamide derivative and is a crystalline, non-hygroscopic, white to brownish powder. The substance is assigned to class II according to the biopharmaceutical classification system . Vismodegib is achiral and polymorphic . The thermodynamically stable modification B is used medicinally.
Vismodegib has anti-tumor properties and is effective orally. It is used for the oral treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma. Vismodegib is teratogenic and must therefore not be used in pregnant women or women of childbearing potential. Since the disease ( basalioma ) mostly occurs in people over the age of 60, this is not a relevant contraindication and probably only affects a few patients.
Mechanism of action
Vismodegib works by inhibiting the Hedgehog signal transduction pathway ( Hedgehog signal pathway , Hh signal pathway). This signaling pathway plays an important role in human embryonic development , where it controls cell growth and differentiation and consequently the size and differentiation of tissues. In the 1990s it was discovered that basal cell carcinomas often have abnormal activation of the Hh signaling pathway, which is normally inactive in adults.
Vismodegib works in the Hh signaling cascade by specifically binding to the transmembrane receptor Smoothened (SMO), a key protein in the Hh signaling pathway. The expression of Hh target genes , many of which at the proliferation involved, survival and differentiation of cells is suppressed.
Clinical information
application areas
Vismodegib is used in adult patients with:
- symptomatic metastatic basal cell carcinoma
- locally advanced basal cell carcinoma for which surgery or radiation therapy is not appropriate
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women; Women of childbearing potential who do not adhere to the Erivedge Contraception Program
- Simultaneous use of St. John's wort
Side effects
The most common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) that occurred in more than 30% of patients were muscle cramps (74.6%), hair loss (65.2%), taste disorders (57.2%), weight loss (48.6%) ), Fatigue (44.9%) and nausea (34.8%).
Early benefit assessment in Germany
Since 2011, newly approved drugs with new active ingredients in Germany have had to undergo an " early benefit assessment " by the Federal Joint Committee (G-BA) based on Section 35a SGB V ( AMNOG ) if the pharmaceutical manufacturer wants to achieve a higher sales price than just the fixed amount . Only if there is an additional benefit can the drug manufacturer negotiate a price with the umbrella association of statutory health insurance funds (GKV-Spitzenverband) . This also applies to vismodegib. In an initial assessment, the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) considers an added benefit of vismodegib to be not proven compared to the ACT. In February 2014, the G-BA made the final decision on the extent of the additional benefit, which concludes the early benefit assessment: “Patients with symptomatic metastatic basal cell carcinoma: an additional benefit has not been proven ; Patients with locally advanced basal cell carcinoma for whom neither surgery nor radiation therapy is suitable: hint of a minor additional benefit ”.
literature
- Registration documentation for Erivedge on the European Medicines Agency (EMA) website
- Aleksandar Sekulic, Michael R. Migden, Anthony E. Oro, Luc Dirix, Karl D. Lewis, John D. Hainsworth, James A. Solomon, Simon Yoo, Sarah T. Arron, Philip A. Friedlander, Ellen Marmur, Charles M. Rudin, Anne Lynn S. Chang, Jennifer A. Low, Howard M. Mackey, Robert L. Yauch, Richard A. Graham, Josina C. Reddy, Axel Hauschild: Efficacy and Safety of Vismodegib in Advanced Basal-Cell Carcinoma. In: New England Journal of Medicine. 366, 2012, pp. 2171-2179, doi: 10.1056 / NEJMoa1113713 .
- John T. Lear: Oral Hedgehog-Pathway Inhibitors for Basal-Cell Carcinoma. In: New England Journal of Medicine. 366, 2012, pp. 2225-2266, doi: 10.1056 / NEJMe1202170 .
- BM Gensthaler, S. Siebenand: New on the market - ponatinib and vismodegib . In: Pharmazeutische Zeitung , issue 36/2013.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c fluorochem.co.uk: Safety vismodegib (PDF) accessed on December 29, 2013.
- ↑ a b Roche: Safety data sheet ERIVEDGE (R) Capsules (150 mg) (PDF) accessed on December 29, 2013.
- ↑ Vismodegib in basal cell carcinoma: added benefit not proven . IQWiG press release, November 15, 2013, accessed on February 6, 2014.
- ↑ Benefit assessment procedure for the active ingredient vismodegib. Decision of the G-BA on the benefit assessment according to Section 35a SGB V, accessed on February 6, 2014.