Vozhod (spaceship)
Woschod [ vasˈxɔt ] (alternative spelling Woßchod , Russian Восход "sunrise", English Voskhod) was the successor project to the Vostok flights as part of the Soviet space flights of the early 1960s. The spaceship was developed by OKB-1 Koroljow ( Experimental-Konstruktionsbüro -1, today RKK Energija ) from the single-seat forerunner Vostok .
The Vozhod program
For the first time, several people flew into earth orbit on a Vozhod spaceship. Before the first start of the Gemini program , the Soviet Union put three men into space. And that in shirt sleeves : for reasons of space, the cosmonauts could not wear pressure suits, which was justified to the public with the high level of security of the new spacecraft. In fact, extreme risks were taken for the crew during take-off on the flights; in the event of an accident on the take-off site or during the first fifty seconds after take-off, there was no possibility of rescue for the crews.
The second manned mission with two cosmonauts was the first to aim for a space exit (EVA). Both astronauts were now wearing spacesuits, including the commander who remained in the pressurized cabin. The Soviet Union was able to beat the Americans by a few weeks again.
The Vozhod spaceship family
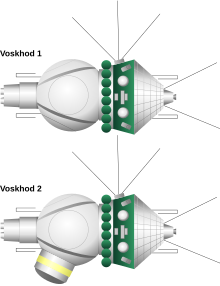
The Vozhod spaceship was not a completely new development, but a modified Vostok spaceship. Improvements to the R-7 launch vehicle made it possible for the Vozhod rocket that was created from it to transport a higher payload into orbit. This enabled the rocket to carry the much heavier Vozhod spaceship. The return without braking maneuvers due to the aerodynamic resistance in the low orbits in the event of a failure of the fluid power unit during the flights of the Vostok was no longer possible before the essential supplies were used up in the multi-seat operation for reasons of capacity. Therefore, there was an additional solid brake engine at the tip of the spaceship. The ejection seat was removed in favor of up to three loungers. These were offset by 90 degrees compared to the previous model, so the space could be used better. However, the instruments kept their original place, so that the crew had to keep turning their heads to the side. At least with the manual landing procedure of the flight from Woschod 2, this should have a disadvantageous effect. While the “3KV” version was intended for three cosmonauts, the “3KD” version offered space for two cosmonauts. This version also had an air lock that could be deployed, which made it possible to exit into the vacuum and was blown off after the mission.
During the landing procedures of the Vostok spaceships, the cosmonauts were catapulted out of the capsule at a height of around seven km after opening the main screen and landed with a parachute. Two or three catapult seats could not be accommodated in the Vozhod spaceships for reasons of space and weight. The crew had to land on board. In order to ensure the smooth landing of the relatively heavy spaceships, solid-state brake rockets were used immediately before touchdown directly above the return capsule in the harness of the main parachute. The method has proven itself and is still practiced in a perfected form in the Soyuz spaceships .
Performed flights
Only two manned flights were carried out, before each an unmanned test flight with a spaceship of the same configuration.
- Kosmos 47 (launched on October 6, 1964): was an unmanned test flight
- Woschod 1 (start on October 12, 1964): manned first flight with the cosmonauts Vladimir Komarow , Boris Jegorow and Konstantin Feoktistow
- Kosmos 57 (launch on February 22, 1965): failed unmanned test flight
- Wozhod 2 (start on March 18, 1965): Flight with Pavel Belyayev and Alexei Leonov , whocarried outthe first space exit.
- Kosmos 110 (start on February 22, 1966): 22-day long-term flight with the dogs "Veterok" and "Ugolyok"
Unrealized flights
A manned long-term flight with Woschod 3, for which Kosmos 110 was carried out as a test flight, was planned, but was repeatedly postponed without ever being canceled. Eventually all efforts were concentrated on the new Soyuz program . Also all other flights planned or considered under Korolev did not take place.
- Woschod 3 : 19-day mission for studies on the effects of long-term stays in weightlessness on the human organism. The flight was postponed several times, never officially canceled, but ultimately did not take place
- Vozhod 4 : 20-day mission
- Wozhod 5 : a 10-day female crewed mission
- Woschod 6 : Test flight to test a control belt for spacecraft operations
- Woschod 7 : Simulation of artificial gravity through connection with the third stage of the rocket and rotation of the entire complex
See also
Web links
- Voskhod - A Summary (English)
- Первые пилотируемые космические корабли "Восток" и "Восход" (Russian)