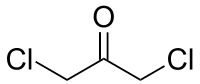
1,3-dichloroacetone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,3-dichloroacetone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 4 Cl 2 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 126.97 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.383 g cm −3 (46 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
39-43 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
172.6-173 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
<0.1 mm Hg (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
little in water (27.9 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
1,3-dichloroacetone is a dichlorinated derivative of acetone . Like other halogenated acetones, it belongs to the group of chlorinated ketones .
properties
1,3-Dichloroacetone is in the form of colorless white crystals at room temperature . It is very soluble in alcohol or diethyl ether . According to Antoine, the vapor pressure function results from log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 4.90009, B = 1937.489 and C = −49.092 in the temperature range from 348 to 445 K. The heat of vaporization is 49.6 kJ · mol −1 . 1,3-dichloroacetone only forms flammable vapor-air mixtures at higher temperatures. The compound has a flash point of 95 ° C, the ignition temperature is 590 ° C.
use
1,3-dichloroacetone is used as the starting material for the production of cyclopropanols and cyclopropanones .
safety instructions
1,3-dichloroacetone is very toxic; it is also absorbed through the skin. In addition to the toxic effect, contact with skin or eyes also causes considerable irritation and even chemical burns.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Hans-Joachim Teuber, Günther Schütz, Eberhard Erkenbrecher: Vinylogous guanidines of the pyrroline series made from “dimeric” chloroacetonitrile. In: Archives of Pharmacy . 313, 1980, pp. 851-858, doi : 10.1002 / ardp.19803131007 .
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on 1,3-dichloroacetone in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Data sheet 1,3-dichloroacetone from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 14, 2014 ( PDF ).
- ↑ David O Hagan, Jeffrey White, David A. Jones: Efficient routes to isotopically labeled epichlorohydrins ((chloromethyl) oxiranes). In: Journal of Labeled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals . 34, 1994, pp. 871-880, doi : 10.1002 / jlcr.2580340908 .
- ↑ Theodor Posner, Karl Rohde: About the so-called pseudo-dichloroacetone, an alleged isomer of the symmetrical dichloroacetone. In: Reports of the German Chemical Society. 42, 1909, pp. 3233-3242, doi : 10.1002 / cber.19090420349 .
- ↑ a b E. D. Smith, WL Thornsberry: Characterization data for chloroacetone, 1,1-dichloroacetone, and 1,3-dichloroacetone . In Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 15 (1970) 296-297, doi : 10.1021 / je60045a002 .
- ↑ RM Stephenson, S. Malanowski: Handbook of the Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds , Springer 1987, ISBN 978-94-010-7923-5 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-94-009-3173-2 .
- ↑ a b Entry on 1,3-dichloro-2-propanone. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 16, 2014.


