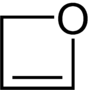
2 H -oxet
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | 2 H -oxet | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Oxacyclobutene |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 4 O | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 56.06 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
2 H -Oxet belongs to the group of heterocyclic chemical compounds . It is the simplest stable oxygen-containing unsaturated four-membered heterocycle . Formally, it is derived from the structure of cyclobutene , in which a carbon atom has been replaced by an oxygen atom.
Extraction and presentation
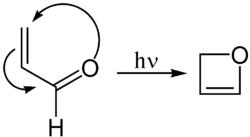
2 H -oxet can be synthesized by a photochemical cyclization of acrolein .
Reactions
By reduction with molecular hydrogen on palladium - activated carbon - catalyst 2 can be H -Oxet to the saturated oxetane reduces be.
It usually reacts with nucleophiles to open the ring, which reduces the high ring tension .
Even at room temperature, Oxet slowly converts to acrolein with ring opening.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ O. Kikuchi in: A classification of the photochemical electrocyclic reactions of heteroatom conjugated systems Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 9, 859-862, doi: 10.1016 / 0040-4039 (81) 80015-9 .
- ↑ a b P. C. Martino, PB Shevlin: Oxetene: synthesis and energetics of electrocyclic ring opening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 16, 5429-5430, doi: 10.1021 / ja00536a069 .