3,4-methylenedioxy -N- ethylamphetamine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
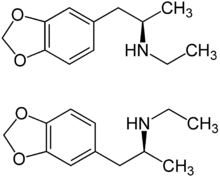
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| ( R ) shape (top) and ( S ) shape (bottom) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 3,4-methylenedioxy -N- ethylamphetamine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 17 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 207.22 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
201–202 ° C (racemate hydrochloride) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
3,4-Methylenedioxy- N -ethylamphetamine ( MDEA or MDE for short ) is a synthetic drug with a very close molecular-structural relationship to MDMA and MDA . It is structurally one of the amphetamines and is chiral , i. i.e., there are two enantiomeric forms ( R ) -MDE and ( S ) -MDE.
synthesis
It can be produced from MDA by acetylation and subsequent reduction with lithium aluminum hydride , or from the corresponding phenylacetone by condensation with ethylamine and subsequent reduction.
Chemical and pharmacological properties
MDE is chiral . There are two enantiomeric forms, the ( R ) form and the mirror image ( S ) form. The free base MDE is an oil and contains the functional group of a secondary amine R 2 NH The free base forms a crystalline hydrochloride R 2 NH · HCl with hydrochloric acid . MDE blocks the absorption of catecholamines ( dopamine , noradrenaline , adrenaline ). The effective dosage is in the range from 100 to 200 mg, the duration of action is in the range from three to six hours.
The effect of MDE on sensory perception is similar to that of MDMA, but is shorter at two to three hours. MDE has primarily a strong entactogenic and weakly empathogenic effect and thus more in an autistic direction and promotes self-focus and the loss of social contacts.
Legal position
Shortly after the ban on MDMA, MDE increasingly appeared on the black market as a substitute substance, which is why it was included with 13 other substances with the 3rd BtMÄndV of February 28, 1991 with effect from April 15, 1991 in Appendix 1 to § 1 BtMG and any handling ( with the exception of consumption) with this substance is prohibited.
Adapted to the WHO nomenclature, the official spelling has been methylenedioxyethylamfetamine ( f instead of ph ) since 1998 .
Additional Information
MDE can be a component of ecstasy tablets , the actual composition of which is usually only known to the manufacturer.
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index. An Encyclopaedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 14th edition, 2006, p. 996, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ a b Data sheet (±) -3,4-Methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine hydrochloride from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 20, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Third Narcotics Act - Amendment Ordinance of February 28, 1991.
- ↑ Narcotics Act (BtMG) , as of December 18, 2009, valid from January 22, 2010.
Web links
- MDE . In: Erowid . (English)
- MDE at PIHKAL
