5-methylcytosine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 5-methylcytosine | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
4-Amino-5-methyl-1 H -pyrimidin-2-one |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 7 N 3 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
crystalline solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 125.13 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
> 270 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
5-methylcytosine is a heterocyclic organic compound with a pyrimidine backbone. It is a derivative of the nucleic base cytosine with an additional methyl group in position 5. This substitution pattern corresponds to the analogy between uracil and thymine . 5-methylcytosine forms the nucleosides 5-methylcytidine (5mC, m 5 C) in the RNA and 5-methyldeoxycytidine ( 5-Me dC) in the DNA .
properties
Physical Properties
5-methylcytosine is a crystalline solid that melts at over 270 ° C.
Chemical properties
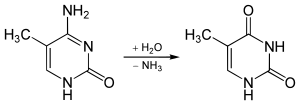
Due to its chemical instability, it can deaminate into thymine .
Biological importance
In addition to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine , 5-formylcytosine and (still controversial) 5-carboxylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine is one of the modified DNA bases found in mammals. Therefore, 5-methylcytosine is often referred to as the fifth and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine is often referred to as the sixth base of DNA. 5-Methylcytosine is formed in vivo post- replicatively (after DNA synthesis) from cytosine by adding a methyl group ( DNA methylation ). This reaction is catalyzed by DNA methyl transferases (DNMTs).
5-methylcytosine plays an important role in epigenetics and is involved in switching genes on and off and probably also in the organization of DNA in chromosomes.
Under physiological conditions, a small part of the deoxycytidine contained in the DNA dehydrates to deoxyuridine , for which special repair systems exist in the cells. When 5-methyldeoxycytidine is deaminated , however, the deoxythymidine , which is also normally contained in the DNA, is produced , which cannot be recognized as faulty, which means that it can pair with deoxyadenosine in the next round of replication , which then results in a transition from deoxycytidine to deoxythymidine and on the opposite DNA strand from deoxyguanosine to deoxyadenosine.
literature
- Melanie Ehrlich, Miguel A. Gama-Sosa, Laura H. Carreira, Lars G. Ljungdahl, Kenneth C. Kuo, Charles W. Gehrke: "DNA methylation in thermophilic bacteria: N 4 -methylcytosine, 5-methylcytosine, and N 6 - methyladenine ", Nucleic Acids Research , 1985 , 13 (4), pp. 1399-1412 ( doi : 10.1093 / nar / 13.4.1399 ; PMC 341080 (free full text); PMID 4000939 ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c data sheet 5-methylcytosine from AlfaAesar, accessed on February 7, 2011 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ GA Wagner: Introduction to Archaeometry , 1st edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin 2007, ISBN 3-540-71936-9 , p. 282.
- ^ JR Siewert, M. Rothmund, V. Schumpelick: Praxis der Viszeralchirurgie: Onkologische Chirurgie , 3rd edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin 2010, ISBN 3-642-03807-7 , p. 71.
- ↑ Anja Naumann, Norbert Hochstein, Stefanie Weber, Walter Doerfler: “5-methylcytosine as an important regulator in genetics” (PDF file; 784 kB).
- ↑ Ralph Remus: Distribution of the fifth DNA base 5-methyl-deoxycytidine in the mammalian genome: DNA methylation patterns of endogenous retroviral sequences of the Syrian hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) and in the promoters of human erythrocyte membrane skeleton proteins (Homo sapiens) , dissertation 2000, University of Cologne ( PDF ) .
Web links
- Entry for 5-methylcytosine in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed September 24, 2013.