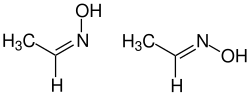
Acetaldehyde oxime
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| ( Z ) -isomer (left) and ( E ) -isomer (right) | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetaldehyde oxime | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Acetaldoxime |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 5 NO | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 59.07 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.969 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
115 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
13 hPa (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.426 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
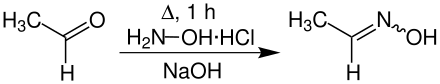
Acetaldehyde oxime is a chemical compound from the group of oximes . It occurs in two stereoisomeric forms ( cis - and trans -).
Extraction and presentation
Acetaldehyde oxime can be obtained by reacting acetaldehyde with hydroxylamine . The synthesis produces a mixture of ( Z ) -isomer and ( E ) -isomer:
In the resulting mixture of isomers, the ( Z ) isomer usually dominates .
properties
Acetaldehyde oxime is a colorless, flammable liquid that is easily soluble in water. It comes in two forms that melt at 12 ° C or 45 ° C. The two stereoisomers both have a planar molecular structure and their energy difference is only 0.7 kcal / mol. The commercially available products have a ( Z ) :( E ) ratio of 10-20: 1. The oxime slowly decomposes at room temperature in air.
use
Acetaldehyde is useful as an intermediate for the synthesis of organic compounds such as pesticides Methom , Thiodicarb , and Alanycarb used.
safety instructions
The vapors of acetaldehyde oxime can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 40 ° C).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on acetaldehyde oxime in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b c Richard P. Pohanish: Sittig's Handbook of Toxic and Hazardous Chemicals and Carcinogens . William Andrew, 2011, ISBN 978-1-4377-7869-4 , pp. 3033 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2001, ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8 , Acetaldoxime, doi : 10.1002 / 047084289x.ra004 / abstract (English).
- ↑ Richard J. Lewis: Hazardous Chemicals Desk Reference . John Wiley & Sons, 2008, ISBN 0-470-33445-2 , pp. 1462 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Data sheet Acetaldehyde oxime, mixture of syn and anti, 99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 15, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Entry on acetaldehyde oxime in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed April 15, 2017.
- ^ A b Charles S. Gibson: Essential Principles of Organic Chemistry . Cambridge University Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-316-60386-4 , pp. 160 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ^ Super Course in Chemistry for the IIT-JEE: Organic Chemistry . 2011, ISBN 81-317-5979-2 , pp. 34 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ wiley.com: Acetaldoxime , accessed April 15, 2017
- ^ Zvi Rappoport, Joel F. Liebman: The Chemistry of Hydroxylamines, Oximes and Hydroxamic Acids . John Wiley & Sons, 2008, ISBN 0-470-74195-3 , pp. 17 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ M. Madalena Caldeira, Victor MS Gil: Self-association and relative stability of the isomeric structures of acetaldoxime. In: Tetrahedron. 32, 1976, p. 2613, doi: 10.1016 / 0040-4020 (76) 88037-4 .