Thiodicarb
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
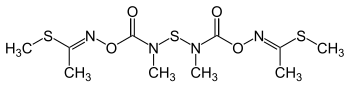
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Thiodicarb | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 N 4 O 4 S 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 354.47 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.4424 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
173-174 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
184.7 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Thiodicarb is an active ingredient for crop protection and a chemical compound from the group of carbamates .
Extraction and presentation
Thiodicarb can be obtained by reacting methomyl with thionyl chloride or sulfur (I) chloride .
properties
Thiodicarb is a white to yellowish solid. It is stable under exposure to light and normal ambient conditions, but can hydrolyze under acidic and basic conditions. The most important breakdown product when thiodicarb is hydrolyzed is methomyl. At elevated temperatures (e.g. over 100 ° C) it essentially decomposes into carbon dioxide , acetonitrile and dimethyl disulfide . The degradation process is catalyzed by heavy metal salts of the Lewis acid type.
use
Thiodicarb is a relatively narrow spectrum non-systemic carbamate insecticide that is closely related to its metabolite methomyl. It works specifically against pests from the butterfly family , specifically on their larvae and eggs. Thiodicarb also suppresses harmful beetles and some peckers, and is primarily used in cotton, corn, and soybeans. The effect is due to inhibition of cholinesterase - enzymes .
Admission
Thiodicarb was first approved in the USA in 1984 and produced by Rhône-Poulenc .
The EU Commission decided in 2007 that thiodicarb should not be included in the list of permitted active ingredients. The decisive factor was the assessment that the use of thiodicarb in the cultivation of table grapes or grapes can lead to an acute health risk for consumers. Approval as a molluscicide was also not granted because too little data was available on the pollution of the user and the risk to the groundwater. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
In Brazil, thiodicarb is approved under the trade name Larvin (Bayer) for use on cotton ( Spodoptera frugiperda and Heliothis virescens), maize (Spodoptera frugiperda) and soy (Anticarsia gemmatalis and Chrysodeixis includens). In 2016 Bayer obtained an extension of the approval for the control of Helicoverpa armigera to include cotton and soy in Brazil.
safety instructions
Thiodicarb is classified as possibly carcinogenic (group B2).
Web links
- EU: Review report for the active substance thiodicarb finalized in the Standing Committee on the Food Chain and Animal Health at its meeting on July 14, 2006 (PDF; 26 kB)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR), Monograph for Thiodicarb , accessed December 9, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Thiodicarb, PESTANAL at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 19, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ FAO: Thiodicarb (PDF; 889 kB)
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 141 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Terry R. Roberts, David H. Hutson, Philip W. Lee, Peter H. Nicholls: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Part 2: Insecticides and Fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 567 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b EPA: RED FACTS THIODICARB (PDF; 24 kB), December 1998
- ↑ 2007/366 / EC: Commission decision of 25 May 2007 on the non-inclusion of thiodicarb in Annex I of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and the revocation of the authorizations for plant protection products with this active substance (announced under file number K (2007 ) 2165) , Official Journal No.L 139 of 31/05/2007 pp. 0028 - 0029
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on thiodicarb in the EU pesticide database; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; Retrieved February 25, 2016.
- ↑ Larvin - Agro Bayer - Inseticida para Cultivos. Retrieved June 14, 2020 (Brazilian Portuguese).
- ↑ Bayer Cropscience do Brasil Ltda: Bayer obtains registration of Larvin 800 WG in Brazil. In: AgNews. January 13, 2016, accessed June 14, 2020 .


