Acrux
|
Double star Acrux (α Crucis) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
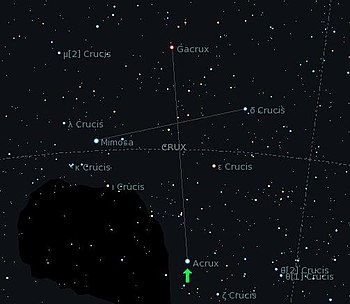
| Acrux to the south of the Southern Cross constellation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AladinLite | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constellation | southern Cross | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | 0.77 mag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Astrometry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| parallax | (10.17 ± 0.67) mas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| distance | (321 ± 21) ly ((98 ± 6) pc ) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Individual data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Names | Aa, Ab; B. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Observation data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Right ascension | Aa, Ab | 12 h 26 m 35.9 s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | 12 h 26 m 36.4 s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| declination | Aa, Ab | −63 ° 05 ′ 56.7 ″ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | −63 ° 05 ′ 58.3 ″ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apparent brightness | Aa, Ab | 1.3 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | 1.6 mag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Typing: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral class | Aa, Ab | B0.5 IV | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | B1 V | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | Aa, Ab | approx 14 + 10 M ☉ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | approx. 13 M ☉ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| radius | Aa, Ab | 8.9 R ☉ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luminosity | Aa, Ab | 25,000 L ☉ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | 16,000 L ☉ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Effective temperature | Aa, Ab | 28,000 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | 26,000 K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotation time | Aa, Ab | 6.3 d | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other names and catalog entries |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acrux is the brightest star in the Southern Cross ( Crux ) constellation and the twelfth brightest in the sky. Since it is very far south, it was not given a proper name in European cultures ; the name Acrux is simply A lpha and Crux formed. In astronomy he is systematically as α Crucis or short α Cru designated in accordance follow Becrux and Gacrux .
With an apparent magnitude of 0.77 mag, it is the southernmost first magnitude star .
In fact, it is a multiple star system located about 320 light years from the solar system. The two optically separable components, α¹ Crucis and α² Crucis, have an angular distance of 4.29 ". Α¹ Cru has an apparent brightness of 1.3 mag, α² Cru of 1.6 mag. Both are hot stars of the spectral class B, with surface temperatures of 28,000 K and 26,000 K and a luminosity of about 25,000 and 16,000 times that of the sun . A circling takes so long that the orbital movement can hardly be made out. From its minimum distance of 430 AU it results at least 1500 years, but is probably much longer.
Α¹ Cru is itself a spectroscopic binary star whose components are assumed to be 14 and 10 times the mass of the Sun. They orbit each other in just 76 days at a distance of about 1 AU.
Another main sequence star of the spectral class B5 V with the designation HR 4729 (or HD 108250), which has an apparent magnitude of 4.8 mag, is about 90 "away from Acrux at a position angle of 202 degrees and has the same spatial direction of movement , therefore it could be gravitationally bound to the Acrux system.According to measurements by the space probe Gaia it is about 309 light years (corresponding to a parallax of 10.5623 milli-arcseconds) from the earth.
The masses of the lighter components of α¹ Cru and α² Cru suggest that they will explode as a supernova at the end of their life cycle . The weaker component of α¹ Cru, on the other hand, could end up as a white dwarf .
The IAU has the proper name on July 20, 2016 Acrux as standardized proper names for α 1 set. However, it is also pointed out that this proper name is only valid for its visually lighter component. The weaker component of α 1 and the star α 2 therefore have no proper names.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ The Tycho-2 catalog of the 2.5 million brightest stars . In: The Smithsonian / NASA Astrophysics Data System (Ed.): Astronomy and Astrophysics . tape 355 , 2000, pp. L27-L30 , bibcode : 2000A & A ... 355L..27H (English). Catalog data at VizieR
- ↑ Gaia Data Release 2 (Gaia DR2), April 2018.
- ↑ Bulletin of the IAU Working Group on Star Names, No. 1, July 2016. (PDF) Retrieved November 9, 2016 (English, 184 KiB).
