Agribusiness

Agribusiness or also agrobusiness refers to as Anglicism (from the English "agriculture" and "business") in addition to agriculture also the economic activities upstream and downstream. Together they form a value chain . This overall system is referred to as agribusiness or agri-food industry , more rarely also as food industry or in English as food chain, food supply chain, food value chain or food system.
The term "agribusiness"
Occasionally, agribusiness also only refers to the area of agriculture and the immediately upstream areas (input industries) and the immediately downstream areas (collection and wholesale). In its predominant meaning, the term agribusiness is broader and encompasses all areas of the value chain up to distribution to the end consumer. The importance of agribusiness thus extends further than the colloquial expression from farm to fork , which is adopted from the English , since agribusiness as a value chain for food also includes the entire area upstream of agriculture. This overall system is of particular importance in connection with food safety and the traceability of food back to its origin. The term is rarely used in English and German with negative connotation as a designation for industrial agriculture .
Components
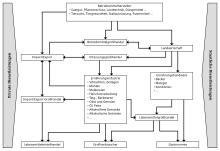
The following economic sectors belong to the overall food economy system:
- Sectors in the area upstream of agriculture :
- Seed breeding, fertilizers , pesticides , agricultural technology , animal breeding , animal feed and compound feed, animal health, stable technology and farm management;
- Sectors in the agricultural sector itself, the production sectors :
- Agriculture , horticulture and ornamentals, viticulture , livestock farming , fishing and aquaculture ;
- Sectors in the downstream area of the capture and wholesale level :
- Grain trade, cattle trade, fruit and vegetable wholesalers, importers, exporters as well as private and cooperative agricultural trade organizations that are engaged in both agricultural procurement and sales;
- Sectors in the so-called first processing stage (processing of the agricultural raw product):
- Grain and grinding mills, peeling mills, oil mills , slaughterhouses and cutting plants, dairies , starch processing, egg products, fish processing, fruit and vegetable processing, malting plants , spice factories , wineries, sugar factories ;
- Sectors in the second processing stage :
- Bread and baked goods, bakery, foodstuffs and pasta, meat products , butcher's trade, confectionery, non-alcoholic beverages, alcoholic beverages, vinegar , other processed products and ready meals in various production and appearance forms;
- Sectors at the grocery level :
- Grocery Retail , Stationary Grocery Wholesale (Cash & Carry), Grocery Delivery Wholesalers, Exporters and Importers ;
- Sectors in the food preparation stage as bulk consumers :
- Classic gastronomy , system catering and hotel business, communal catering (companies, hospitals, schools etc.), service companies (catering)
- The system of the food industry also includes the diverse services that are provided within the listed sectors, for example consulting services, financing, transport and laboratory services, insurance , expert reports, etc. through to association activities and state activities.
- The sectors of the first and second processing stage are referred to in official statistics as the producing food industry. This includes the nutrition or food industry and the food trade .
Special case of renewable raw materials
In the context of energy generation from renewable raw materials as well as other economic uses ( phytopharmaceuticals , bio-based plastics, etc.), the non-food area is becoming increasingly important at the processing stage . Among other things, agricultural and forestry products are used to generate energy. Examples include wood or grain combustion , biogas , biodiesel , bioethanol, etc.
The forestry as a timber supplier is usually not associated with the system of the agribusiness, since they conventionally not used for food production. If agriculture changes at least partially from food supply to energy supply and forestry also takes on an important role in the supply of energy through renewable energy , this can be reconsidered.
Market data and employees
In total, around 5.4 million people are employed in the agricultural and food industry in Germany (corresponds to 13 percent of all employees). The gross value added in this sector in Germany is around 157 billion euros (corresponds to seven percent of the gross domestic product (2012)).
Employees:
| Area | Section | Employees approx. |
| Input sectors of agriculture | Agricultural engineering industry | 26,000 |
| Agricultural machinery trade and craft | 45,000 | |
| Plant breeding | 10,000 | |
| Animal breeding (animal genetics) | 8,000 | |
| Feed | 15,000 | |
| Agricultural advice | 15,000 | |
| State Agricultural Administration | 15,000 | |
| Fertilizers , pesticides , animal health | k. A. | |
| Wholesale (reference business) | Wholesale of agricultural raw materials | 64,050 |
| Agriculture | Agriculture , horticulture , viticulture , animal husbandry ... | 668,000 |
| Wholesale and capture trade | only partially surveyable (partially in the case of wholesale of agricultural raw materials) | k. A. |
| Manufacturing | food industry | 555,000 |
| Food crafts | 564,000 | |
| Grocery trade | Grocery retail | 1,300,000 |
| Food Wholesale | 269,800 | |
| Out-of-home market | Gastronomy, catering , canteens and catering etc. | 2,100,000 |
criticism
In addition to general goals that are critical of industry or capitalism, critics of the branch of industry also pursue some that are specifically linked to the subject of agribusiness and food production. Along all target dimensions, non-governmental organizations have formed which politically demand the strengthening of the protected goods they represent. Many of the protection categories have - to varying degrees - found their way into state regulations. The most important protection categories include:
- Animal welfare : The largest and economically most important part of the food industry deals with the processing of animal products. The upstream animal husbandry in the food-value chain of food production is often criticized, especially with regard to husbandry conditions in laying hen husbandry , for fattening poultry and fattening pigs. Representative is z. B. the animal welfare association .
- Environment and nature conservation : Closely linked to the subject of animal welfare, this motive aims at the protection and preservation of limited natural resources in general, e.g. B. on avoiding long transport routes or avoiding disposable packaging. Ultimately, this also includes criticism of the use of genetic engineering in agriculture, as it threatens other species. Representatives are e.g. B. various environmental protection organizations .
- Consumer health protection : This motivation aims to protect against health threats from excessive daily consumption of sugar, fat, salt, etc. as well as protection against food scandals . This applies to both hygiene and questions of permitted and prohibited ingredients in food and its preliminary products (e.g. feed used, animal medication, pesticides). Representatives are e.g. B. Foodwatch .
- Economic consumer protection: This is about preventing economic damage to the consumer, for example by avoiding deception about ingredients and weight or adhering to standards / quality classes or regulations. Economic consumer protection always has a competition law dimension insofar as it allows companies to act on monitored market rules. Representatives are e.g. B. the consumer associations .
- Protection against the unfair consequences of globalization: Appropriately oriented protection organizations work to prevent producers in developing countries from being discriminated against compared to stronger trading partners in industrialized countries. In some cases, seals of approval are developed in order to be able to identify positive examples as role models. Ultimately, this category also includes all other protective interests that relate to the unfair consequences of globalization, such as B. social standards, child labor, etc. Representative is z. B. Transfair .
- Occupational health and safety of workers in industrial agriculture . Agricultural workers' unions such as z. B. United Farm Workers founded by César Chávez in the USA.
- Self-organization of farmers in developing countries: In numerous countries, peasant movements have emerged that have set themselves the goal of defending the smallholder way of life and promoting sustainable agriculture. They and similar movements in the industrialized countries are organized in Via Campesina .
- Finally, as a special case, there is the protected item “taste”. As a countermovement to an increasingly industrialized consumer culture, clubs and organizations that deal with the discovery of the enjoyment of non-industrially produced food are very popular. In contrast to the other protection categories, there is of course no political debate about taste. Representatives are e.g. B. Clubs like Slow Food .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Our food industry. Retrieved July 31, 2014 .
- ^ Economic importance of agriculture (farmers' association based on the Federal Statistical Office). Retrieved May 2, 2014 .