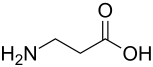
β-alanine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | β-alanine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 7 NO 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 89.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.44 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
200 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
readily soluble in water: 545 g l −1 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
β-alanine is the biogenic amine of the proteinogenic amino acid aspartic acid . β-alanine is itself also an amino acid and structurally a constitutional isomer of the proteinogenic amino acid α- alanine and also the only known naturally occurring β-amino acid.

The difference between the two lies in the position of the amino group : alanine is an α-amino acid, the amino acid group is located on the α-carbon atom (this is the first carbon atom after the carboxy carbon atom). β-Alanine is a β-amino acid, the amino group is located on the β-carbon atom (the second carbon atom after the carboxy carbon atom). Hence the name of this amino acid.
β-Alanine is the simplest representative of the β-amino acids and a degradation product of the pyrimidine bases. β-alanine and pantoic acid react to pantothenic acid , which in turn in coenzyme A is contained.
use
In recent years, β-alanine has become increasingly popular as a dietary supplement to stimulate muscle growth in fitness and bodybuilding, as well as to prevent muscle loss in old age. Studies on the effectiveness of β-alanine suggest a potential positive effect, but potential harmful side effects have not yet been adequately investigated.
Basically, β-alanine is required for the synthesis of the dipeptide carnosine , which consists of β-alanine and histidine . The β-alanine is the speed-limiting component. Carnosine is found in high concentrations in muscle tissue, and especially in type II muscle fibers for rapid maximum loads (e.g. sprinting). It probably serves primarily as a pH - buffer to neutralize during anaerobic activity and avoid acidification, it also acts as an antioxidant and against glycation .
In fact, taking β-alanine can increase intramuscular carnosine concentrations, but only 3–6% of the ingested β-alanine reaches the muscle fibers. Nevertheless, muscle performance can also be increased with a dietary supplement.
β-alanine is used for the synthesis of β-peptides .
N- Alkyl-β-aminopropionic acids are derivatives of the amino acid β-alanine with a wide range of cosmetic and technical applications.
admission
With the natural balanced diet, mainly through the consumption of meat and fish products , an average of 400 mg of β-alanine is consumed daily, while vegetarians do not consume β-alanine through their diet.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on BETA-ALANINE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on April 18, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Β-alanine (PDF) from Merck , accessed on December 19, 2019.
- ↑ Quesnele JJ, Laframboise MA, Wong JJ, Kim P, Wells GD .: The effects of beta-alanine supplementation on performance: a systematic review of the literature in Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014 Feb; 24 (1): 14-27, doi : 10.1123 / ijsnem.2013-0007 .
- ↑ a b Laura Blancquaert, Wim Derave: Bêta-alanine et performances sportives Ortho-Rhumato (Belgique), Volume 13, Issue 6 from December 2015, pages 6-10.