Blue sun nymph
| Blue sun nymph | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||
| Heliangelus regalis | ||||||||||
| Fitzpatrick , Willard & Terborgh , 1979 |
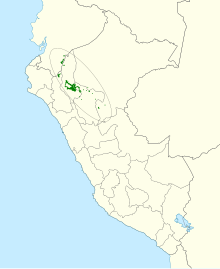
The blue sun nymph ( Heliangelus regalis ) or sometimes also king nymph or king sun nymph is a species of bird from the hummingbird family (Trochilidae). The species has a relatively small range in the north of the South American country Peru . This makes the species endemic . The stock is on the IUCN as endangered ( Endangered estimated).
features
The blue sun nymph reaches a body length of about 11-12 centimeters. The straight black beak is about 14 millimeters long. The male's plumage is characterized by its continuous ultramarine and particularly shimmers on the crown. The long tail is pronounced fork-shaped. The female is very different, so the sexes are dichromatic . The upper part of the female is dark green, the lower part cinnamon with green flecks. It also has a pale chest band. The black-blue, forked tail is much shorter than that of the male.
habitat
The habitat is limited to stunted moist forest areas and areas with scrub. Here the bird prefers sandy soils or sandstone on overhangs. It moves at altitudes between 1350 and 2200 meters, depending on the region.
Subspecies
At the moment, two subspecies of the blue sun nymph are known.
- Heliangelus regalis regalis Fitzpatrick , Willard & Terborgh , 1979 - The nominate form is common in the regions of Cajamarca and San Martín in northern Peru.
- Heliangelus regalis johnsoni Graves , Lane , O'Neill & Valqui , 2011 - This subspecies is found in the Cordillera Azul in Loreto in northern Peru. In contrast to the nominate shape, they shimmer indigo blue, especially on the top of the head, throat and upper chest area . While the control springs at H. r. regalis are purple in color, they are at H. r. johnsoni colored metallic indigo blue in both sexes.
behavior
The male blue sun nymph moves at higher altitudes than the female, especially in the dry season. The bird gets its food from a wide variety of plants, whereby Brachyotum quinquenerve , a plant that belongs to the black- mouthed family , is preferred. Bog bed plants are also popular because they are home to a particularly large number of insects.
Etymology and history of research
John Weaver Fitzpatrick, David Ela Willard and John Whittle Terborgh described the species under the current name Heliangelus regalis . The type specimen was collected by Fitzpatrick on July 14, 1976 in the Cordillera del Cóndor near San José de Lourdes . "Heliangelus" is derived from the Greek words "hēlios ἥλιος " for "sun" and "angelos ἄγγελος " for "angel, messenger, messenger". The specific epithet »regalis« is derived from the Latin words »regalis, rex, regis« for »royal, king«. »Johnsoni« is dedicated to the American ornithologist Ned Keith Johnson (1932–2003).
literature
- Thomas Scott Schulenberg , Douglas Forrester Stotz , Daniel Franklin Lane, John Patton O'Neill , Theodore Albert Parker III : Birds of Peru . Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey 2007, ISBN 978-0-7136-8673-9 .
- James A. Jobling: Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names . Christopher Helm, London 2010, ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4 .
- John Weaver Fitzpatrick, David Ela Willard, John Whittle Terborgh: A new species of hummingbird from Peru . In: The Wilson Bulletin . tape 91 , no. 2 , 1979, p. 177–186 ( online (PDF file; 594 kB) [accessed July 3, 2014]).
- Gary Russell Graves, Daniel Franklin Lane, John Patton O'Neill, Thomas Valqui: A distinctive new subspecies of the Royal Sunangel (Aves: Trochiliformes; Heliangelus regalis) from the Cordillera Azul, northern Peru . In: Zootaxa . No. 3002 , 2011, p. 52–58 ( online (PDF file; 862 kB) [accessed July 3, 2014]).
Web links
- Heliangelus regalis inthe IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014.1. Listed by: BirdLife International, 2012. Retrieved June 28, 2014.
- BirdLife International: Species Factsheet - Royal Sunangel ( Heliangelus regalis ) . Retrieved June 28, 2014.
- Videos, photos and sound recordings for Royal Sunangel (Heliangelus regalis) in the Internet Bird Collection
- Blue sun nymph ( Heliangelus regalis ) at Avibase; accessed on June 28, 2014.
- Heliangelus regalis in the Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ITIS). Retrieved June 28, 2014.
- xeno-canto: Sound recordings - Royal Sunangel ( Heliangelus regalis )