Bromohydroquinone
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Bromohydroquinone | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 5 BrO 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 189.01 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
112-116 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
8.67 / 10.68 |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
water soluble |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Bromhydroquinone is a chemical compound that belongs to the group of phenols . It has been detected in living things as a metabolite of bromobenzene and 2-bromophenol .
presentation
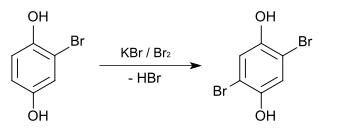
Bromohydroquinone can be prepared by simply brominating hydroquinone with potassium bromide and bromine .
Synthesis by means of Elbs oxidation from 2-bromophenol is also possible.
proof
Methylation with dimethyl sulfate gives 2-bromo-1,4-dimethoxybenzene (CAS number: 25245-34-5), which boils at 262-263 ° C. Complete bromination with potassium bromide and bromine results in 2,5-dibromohydroquinone , the melting point of which is 186 ° C.
The bromohydroquinone diacetate melts at 71-73 ° C.
use
Individual evidence
- ^ Entry on Bromhydroquinone at ChemicalBook , accessed on September 19, 2011.
- ↑ a b c data sheet bromohydroquinone from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 14, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c Dictionary of organic compounds ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ SS Lau, TJ Monks, JR Gillette: "Identification of 2-bromohydroquinone as a metabolite of bromobenzene and o-bromophenol: implications for bromobenzene-induced nephrotoxicity", in: Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics , 1984 , 230 , pp. 360-366 ; PMID 6747840 .
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 331.
- ↑ K. Elbs: "About Nitrohydroquinone", in: J. Prakt. Chem. , 1893 , 48 , pp. 179-185; doi : 10.1002 / prac.18930480123 .
- ^ Association of authors: Organikum , 19th edition, Johann Ambrosius Barth, Leipzig · Berlin · Heidelberg 1993, ISBN 3-335-00343-8 , p. 653.
- ^ JY Savoie, P. Brassard: Sur les présumés cis-Dihalogénures de quinones . In: Canadian Journal of Chemistry . 44, 1966, pp. 2867-2872, doi : 10.1139 / v66-426 .