Brotizolam
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
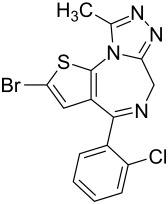
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Brotizolam | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
2-Bromo-4- (2-chlorophenyl) -9-methyl-6 H -thieno [3,2- f ] - s -triazolo [4,3- a ] [1,4] diazepine |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 10 BrClN 4 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 393.69 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
212-214 ° C |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Brotizolam is a benzodiazepine analog from the group of thienodiazepines and, like all its analogs, has amnestic , anxiolytic , anticonvulsant , hypnotic , sedative and central muscle relaxant effects.
application areas
It is used for the short-term treatment of severe problems falling asleep and staying asleep. It is a preparation with a medium-long duration of action. It is used in cattle fattening to increase appetite .
Pharmacokinetics
Brotizolam is rapidly metabolised by CYP3A4 after ingestion . However, brotizolam itself is much more potent than its poorly performing metabolite. The half-life is approx. 4-6 hours. 65% of the elimination takes place after renal excretion.
Pharmacodynamics
Brotizolam has an agonistic effect on the GABA A receptor by influencing the Cl influx of the chloride channels. As a result, the chloride channel is open longer, which leads to hyperpolarization due to the inflowing GABA . Since brotizolam is a thienodiazepine, it can be counted among the most potent benzodiazepines.
Side effects
The most well-known side effects include: drowsiness , headache , vertigo , anterograde amnesia , gastrointestinal disorders, tendency to fall and addiction
Interaction potential
There is potential for interaction with antipsychotics or neuroleptics with low affinity, opioids such as morphine and piritramide . Interactions can also occur with CYP3A4 inhibitors and CYP3A4 inducers, e.g. B. with erythromycin and itraconazole . In addition, with drugs that are used for hypertension : clonidine , metoprolol . Others: trazodone , risperidone , antihistamines of the first generation, as well as all drugs that trigger a GABA-ergic increase or excitatory decrease in the central nervous system .
Use of brotizolam with some restrictions
Due to the very high dependency potential arising from brotizolam, a period of two weeks in therapy should not be exceeded. Then a slow withdrawal ("tapering off") must take place.
Indication of brotizolam
Brotizolam should never be given for simple sleep disorders.
Trade names
Brotizolam is sold under the trade names Lendormin and Lendorm .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; P. 1454, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ R. Mandrioli, L. Mercolini, MA Raggi: Benzodiazepine metabolism: an analytical perspective. In: Current drug metabolism. Volume 9, Number 8, October 2008, pp. 827-844, PMID 18855614 .
- ^ Stiftung Warentest : Suitable prescription sleeping pills , August 15, 2003.
- ↑ Felix R. Althaus: Textbook of pharmacology and toxicology for veterinary medicine. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2010, ISBN 978-3-830-41079-9 , p. 146.
- ^ A b J. K. Aronson: Meyler's Side Effects of Psychiatric Drugs. Elsevier, 2009, ISBN 978-0-444-53266-4 , p. 399 ( limited preview in Google book search).
- ↑ Instructions for use