Cosmic Background Explorer
| Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Research satellite |
| Country: |
|
| Operator: | NASA |
| COSPAR-ID : | 1989-089A |
| Mission dates | |
| Dimensions: | 2265 kg |
| Size: | 5.49 m high |
| Begin: | November 18, 1989, 14:34 UTC |
| Starting place: | Vandenberg Air Force Base SLC-2W |
| Launcher: | Delta-5920-8 D189 |
| Status: | In orbit |
| Orbit data | |
| Rotation time : | 102.6 min |
| Orbit inclination : | 98.9 ° |
| Apogee height : | 886 km |
| Perigee height : | 873 km |
The Cosmic Background Explorer ( COBE ) is a NASA satellite that delivered revolutionary results for measuring cosmic background radiation from 1989 to 1993 . The satellite is still in orbit, it is orbiting the earth at an altitude of approx. 900 km in a polar orbit .
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) space probe was the successor to the satellite and served from 2001 to 2010 to research this radiation. Finally, from August 2009 to 2013, the European Planck space probe measured the radiation with an even greater resolution.
Mission history
Originally, COBE was supposed to be transported into space with the space shuttle . The STS-82-B mission was supposed to start in 1988 from Vandenberg Air Force Base with the Discovery, which was canceled due to the Challenger disaster . COBE was launched on November 18, 1989 on a Delta 5920 launcher .
On September 1, 1990, COBE's supply of liquid helium ran out, which resulted in the failure of some of the instruments, especially FIRAS ( Far Infrared Absolute Spectrophotometer ) for determining background radiation. The scientific mission ended on December 23, 1993; from January 1994, more technological experiments were carried out with the satellite.
Results
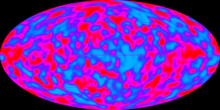
With the help of the Cosmic Background Explorer, a 360 ° map of the cosmic background radiation could be made. The big bang theory was supported.
Further results of the mission are data on interplanetary dust and the position of our sun in the galaxy. In 2006 George Smoot received the Nobel Prize in Physics as scientific director of this program together with John C. Mather , who also worked on this project .
See also
Web links
- Page NASA to COBE (English)
- The Irony of NASA's Nobel . New York Times , October 5, 2006. (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Orbit data according to Mark Wade: COBE in the Encyclopedia Astronautica , accessed on March 16, 2012 (English).
