Calcium thiosulfate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
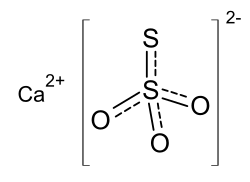
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Calcium thiosulfate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Calcium thiosulphate |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CaO 3 S 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
crystalline colorless solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 152.19 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.87 g cm −3 (hexahydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
45 ° C (hexahydrate, decomposition) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Calcium thiosulphate is an inorganic chemical compound of calcium from the group of thiosulphates .
Extraction and presentation
Calcium thiosulphate can be obtained by reacting sodium thiosulphate with calcium chloride.
The hexahydrate can be obtained from thiosulfuric acid .
The compound can also be prepared by reacting calcium sulfite and sulfur at 30-40 ° C or from boiling lime and sulfur in the presence of sulfur dioxide .
It is also possible to display it by boiling calcium hydroxide with sulfur and water, whereby calcium pentasulfide and calcium thiosulfate are formed first.
properties
Calcium thiosulphate is a crystalline solid that is soluble in water as a hexahydrate. It decomposes when heated above 45 ° C. The hexahydrate has a triclinic crystal structure with the space group P 1 (space group no.2 ) with the cell dimensions a = 7.42 ± 0.01, b = 9.48 ± 0.01, c = 15.19 ± 0.01 Å, α = 128.7 ± 0.3, β = 100.1 ± 0.3, γ = 143.1 ± 3 °. The hexahydrate gives off four parts of water of crystallization at 45 ° C and the remaining two at 85 ° C. The anhydrate decomposes at 112 ° C to calcium sulphate , sulfur and sulfur dioxide .
use
Calcium thiosulfate is used as a herbicide . It is commercially available as a solution, the clear solution having little odor and a pH in the range of 6.5-7.5. It is used for dechlorination, ozone and hydrogen peroxide quenching, in concrete and cement formulations, photographic processes, coatings, stabilizers and reactants for precious and base metals. It is also used as "liquid lime" in agriculture. Calcium thiosulfate is a reducing agent . It is routinely used as a titrant to determine the concentration of oxidants such as hypochlorite in bleach and dissolved oxygen in water. It instantly dechlorinates water and is used to stop a bleaching reaction in the paper industry. It is also used in gold and silver ore processing ( kiss process ). The compound is also used to treat dermatitis and jaundice caused by arsphenamine .
Individual evidence
- ↑ C. Arnold, G. Christ, K. Dietrich, Ed. Gildmeister, P. Janzen, C. Scriba, B. Fischer, C. Hartwich: Hager's Handbook of Pharmaceutical Practice For Pharmacists, Doctors, Druggists and Medicinal Officials. First volume . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-47350-0 , pp. 576 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e Entry on calcium thiosulphate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on April 5, 2019(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . CRC Press, 2016, ISBN 978-1-4987-5429-3 , pp. 54 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d Richard C. Ropp: Encyclopedia of the Alkaline Earth Compounds . Newnes, 2012, ISBN 0-444-59553-8 , pp. 159 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ H. Ballczo, O. Kaufmann: Calcium thiosulfate . In: Monthly magazine for chemistry. 80, 1949, p. 220, doi : 10.1007 / BF00906465 .
- ↑ Entry on Calcium thiosulfate in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed April 5, 2019.
- ↑ Y. Elerman, A. Aydin Uraz u. a .: Crystal data for calcium and nickel thiosulphate hexahydrates: CaS2O3.6H2O and NiS2O3.6H2O. In: Journal of Applied Crystallography. 10, 1977, p. 362, doi : 10.1107 / S0021889877013673 .
- ↑ Peter Held, Ladislav Bohatý: Calcium and strontium thiosulfate, CaS2O3-6H2O and SrS2O3-5H2O. In: Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 60, 2004, p. I97, doi : 10.1107 / S0108270104017986 .
- ↑ Nicholas P. Cheremisinoff, Paul Rosenfeld: Handbook of Pollution Prevention and Cleaner Production Vol. 3: Best Practices in the Agrochemical Industry . William Andrew, 2010, ISBN 978-1-4377-7825-0 , pp. 98 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Mike D. Adams: Gold Ore Processing Project Development and Operations . Elsevier, 2016, ISBN 978-0-444-63670-6 , pp. 498 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Carl Schnabel: Handbuch der Metallhüttenkunde first volume. Copper - lead - silver - gold . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-50720-5 , pp. 947 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Robert Alan Lewis: Lewis' Dictionary of Toxicology . CRC Press, 1998, ISBN 978-1-56670-223-2 , pp. 217 ( limited preview in Google Book search).

