Ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 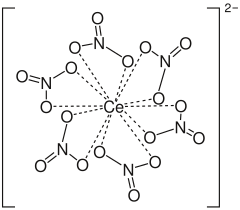
|
||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
monoclinic |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
P 2 1 / n (No. 14, position 2) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 1306.1 ± 0.7 pm, |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | (NH 4 ) 2 [Ce (NO 3 ) 6 ] | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
orange solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 548.26 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
Solid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.490 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
108 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Ammonium cer (IV) nitrate (also cerium (IV) ammonium nitrate , abbreviated CAN ) is an inorganic compound with the formula (NH 4 ) 2 [Ce (NO 3 ) 6 ]. It is an orange-red crystalline solid and is readily soluble in water. The compound is used as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis and in quantitative analysis ( oxidimetry ).
presentation
The anionic complex [Ce (NO 3 ) 6 ] 2− is produced by the conversion of Ce 3+ ions e.g. B. obtained by oxidation with boiling nitric acid . In the presence of ammonium nitrate , ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate is formed. The ammonium cation is not involved in the oxidation processes of ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate.
properties
Ce 4+ is a strong oxidizing reagent (E ° ~ 1.61 V against the normal hydrogen electrode ) and is even stronger than elemental chlorine (E ° ~ 1.36 V). During the redox reaction, Ce (IV) is reduced to Ce (III) by a one-electron transfer and the color of the aqueous solution changes from orange to a pale yellow color (provided, of course, that the reactants have no inherent color).
use
Oxidizing agent
Ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate is a frequently used oxidizing agent for the oxidation of various functional groups. These include alcohols , phenols and ethers . C – H bonds can also e.g. B. be oxidized in benzyl positions . The oxidation of catechols and hydroquinones yield the corresponding quinones .
Protecting chemistry
In protecting group chemistry, ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate is used for the cleavage of p- methoxy and 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl ethers. The aromatic is split off from the protected alcohol via a quinomethine intermediate.
The reaction mechanism is believed to be the same as that for deprotection with DDQ as the oxidant. The oxidizing agent (CAN or DDQ) is reduced by absorbing a total of two electrons (two CAN molecules are involved in CAN) and the benzyl ether reacts to form the corresponding aldehyde with oxidation and water attachment.
Etching of chrome
When structuring thin films , ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate is used for the selective etching of chromium . The chromium is oxidized by the cerium and thus brought into solution. A solution of approx. 10% ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate in an acid ( nitric , perchloric or acetic acid ) has an etching rate of approx. 50–150 nm / min.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d Thomas A. Beinke, J. Delgaudio: Crystal structure of ceric ammonium nitrate . In: Inorganic Chemistry . tape 7 , no. 4 , 1968, p. 715-721 , doi : 10.1021 / ic50062a020 .
- ↑ Preetam Singh, MS Hegde: Controlled synthesis of nanocrystalline CeO 2 and Ce 1 - x M x O 2 −δ (M = Zr, Y, Ti, Pr and Fe) solid solutions by the hydrothermal method: Structure and oxygen storage capacity . In: Journal of Solid State Chemistry . tape 181 , no. 12 , 2008, p. 3248-3256 , doi : 10.1016 / j.jssc.2008.08.018 .
- ↑ a b c data sheet ammonium cerium (IV) nitrate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 3, 2012.
- ↑ Veli T. Kasumov, Ali ©. Öztürk, Fevzi Köksal: Synthesis, characterization and redox behavior of bis (N-1-adamantanyl- and N-2-adamantanyl-3,5-tBu2-salicylaldiminato) copper (II) complexes . In: Polyhedron . tape 26 , no. 13 , 2007, p. 3129-3135 , doi : 10.1016 / j.poly.2007.02.012 .
- ↑ a b Entry on diammonium hexanitratocerate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ G. Brauer: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry , Vol. 2, Academic, New York 1965.
- ↑ Vijay Nair, Lakshmi Balagopal, Roshini Rajan, Jessy Mathew, "Recent Advances in Synthetic Transformations Mediated by Cerium (IV) Ammonium Nitrate", in: Acc. Chem. Res. , (2004), 37, pp. 21-30 ( doi : 10.1021 / ar030002z ).
- ↑ Vijay Nair, Sreeletha B. Panicker, Latha G. Nair, Tesmol G. George, Anu Augustine: "Carbon-Heteroatom Bond-Forming Reactions Mediated by Cerium (IV) Ammonium Nitrate: An Overview", in: Synlett , (2003) , Pp. 156-165 ( doi : 10.1055 / s-2003-36775 ).
- ↑ Phillip J. Kocienski: Protecting Groups , 1st edition, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1994, ISBN 3-13-135601-4 .
- ↑ Microchemicals: Etching of Chromium ( PDF ).





