Chelidamic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Tautomeric boundary structures | |||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chelidamic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 NO 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to yellowish solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | |||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
267 ° C (decomposition, monohydrate) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
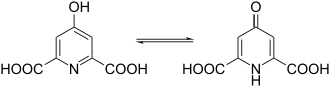
Chelidamic acid is a chemical compound from the group of heterocycles . It consists of a pyridine ring with carboxy groups in the 2- and 6-position and a hydroxyl group in the 4-position.
properties
Chelidamic acid is a white to slightly yellowish compound. It crystallizes out as a monohydrate from aqueous solution. Chelidamic acid monohydrate decomposes at 267 ° C. Chelidamic acid has two tautomeric forms, an aromatic enol form and a keto form . The monohydrate forms a zwitterionic structure in the crystal . In this one carboxylic acid group is deprotonated and the nitrogen is protonated.
Manufacturing
Chelidamic acid can be produced by reacting chelidonic acid with ammonia .
use
Chelidamic acid can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. The hydroxy group can easily be substituted . The carboxylic acid groups can be used to build larger structures.
Chelidamic acid forms stable complexes with many metal ions . It acts as a tridentate chelating ligand .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Chelidamic acid hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ AK Hall, JM Harrowfield, BW Skelton, AH White: Chelidamic acid monohydrate: the proton complex of a multidentate ligand , in Acta. Cryst. 2000 , C56 , pp. 448-450; doi: 10.1107 / S0108270199015620 .
- ↑ L. Haitinger, A. Lieben: Investigations on chelidonic acid , in: Monatsh. Chem. 1885 , 6 , pp. 279-328; doi: 10.1007 / BF01554631 .
- ↑ MK Tse, S. Bhor, M. Klawonn, G. Anilkumar, H. Jiao, C. Döbler, A. Spannenberg, W. Mägerlein, H. Hugl, M. Beller: Ruthenium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Epoxidation of Olefins Using H2O2, Part I: Synthesis of New Chiral N , N , N -Tridentate Pybox and Pyboxazine Ligands and Their Ruthenium Complexes , in: Chemistry 2006 , 12 , pp. 1855-1874; doi: 10.1002 / chem.200501261 .

