Chelidonic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chelidonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
4-Oxo-4 H -pyran-2,6-dicarboxylic acid ( IUPAC ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 4 O 6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light red powder |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 184.10 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
265 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
moderately in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Chelidonic acid is a heterocyclic organic dicarboxylic acid . It has a pyran framework.
history
While investigating the herb and the roots of the celandine , JMA Probst discovered chelidonic acid in 1839. Lerch (1846), Hutstein (1851) and Wilde (1863) subsequently published the results of their research.
presentation
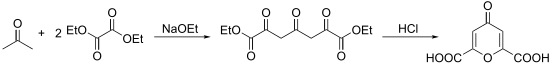
To produce chelidonic acid, acetone is first reacted in a double Claisen condensation with diethyl oxalate . Sodium ethanolate is conveniently used as the base . The resulting 2,4,6-trioxo-1,7-dicarboxylic acid diethyl ester can then be cyclized to chelidonic acid using aqueous hydrochloric acid .
properties
Chelidonic acid is a colorless and odorless solid that melts at 265 ° C. It dissolves poorly in water.
Reactions
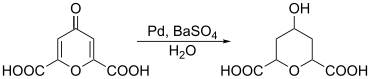
By reduction , chelidonic acid can be used to produce 2,6-pyranedicarboxylic acids. A palladium catalyst , for example, can be used for the reduction .
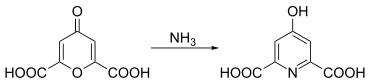
Chelidonic acid reacts with amines to form hydropyridinedicarboxylic acid derivatives. Chelidamic acid can be obtained from chelidonic acid by reacting it with ammonia .
If primary amines (e.g. ethylamine ) are used instead of ammonia , N - alkylated pyridine derivatives can be obtained:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Chelidonic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 7, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ^ Frank Humphreys Storer: First Outlines of a Dictionary of Solubilities of Chemical Substances . Sever and Francis, 1864, p. 125 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Dr. Probst . Description and method of representation of some of the substances newly discovered during the analysis of Chelidonium majus . In: Annalen der Pharmacie , Volume XXIX (1839), pp. 116-120: Chelidonic acid (digitized version)
- ^ Joseph Udo Lerch (1816-1892). Investigation of chelidonic acid . In: In: Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie , Volume LVII (1846), pp. 273-318 (digitized version )
- ↑ J. Hutstein in Breslau. Representation of chelidonic acid . In: Archives of Pharmacy . Second series volume LXV (1851), pp. 23–24 (digital copy)
- ↑ C. Wilde. About chelidonic acid . In: Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie , Volume CXXVII (1863), 2nd issue pp. 164–170 (digitized version )
- ↑ August Husemann and Theodor Husemann : The plant substances in chemical, physiological, pharmacological and toxicological terms. For doctors, pharmacists, chemists and pharmacologists. Springer, Berlin 1871, pp. 782-786: Chelidonic acid . Chelidonic acid. Chelidoxanthin. (Digitized version)
- ↑ G. Horvath, C. Russa, Z. Koentoes, J. Gerencser, Synth. Comm. , 1999 , 29 , 21, pp. 3719-3732.
- ↑ David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-0595-5 , pp. 446 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Attenburrow, J. Chem. Soc. , 1945 , pp. 571-574.
- ↑ DG Markees, J. Org. Chem. , 1958 , 23 , p. 1030, doi : 10.1021 / jo01101a025 .