Chinalphos
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
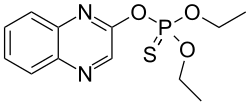
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chinalphos | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 15 N 2 O 3 PS | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 298.30 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.235 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
31-32 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
142 ° C (at 0.0003 mbar, decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
practically insoluble in water (27 mg l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Quinalphos is a chemical compound from the group of organophosphates and thiophosphoric acid esters and an insecticide introduced by Bayer AG (now Bayer CropScience ) in 1969 .
Extraction and presentation
Quinalphos can be obtained by reacting o -phenylenediamine with dichloroacetic acid and then with DEPCT .
properties
Quinalphos is a flammable colorless solid that is practically insoluble in water. It hydrolyzes easily, except in slightly basic conditions.
use
Quinalphos is used as an insecticide on a number of crops against biting and sucking pests. The methyl form (quinalphos-methyl, CAS number: 13593-08-3) is also used as a pesticide.
Admission
In the European Union, quinalphos is not included in the list of permitted active ingredients in pesticides. In Germany, Austria and Switzerland, no pesticides with this active ingredient are permitted.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l Entry on Chinalphos in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 10, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Entry on Quinalphos in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Thomas A. Unger: Pesticide Synthesis Handbook . William Andrew, 1996, ISBN 0-8155-1853-6 , pp. 604 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ A b Erwin Deutsch, Hans-Dieter Lippert: Metabolic Pathways of Agrochemicals: Insecticides and fungicides . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1999, ISBN 0-85404-499-X , pp. 480 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Regulation (EC) No. 2076/2002 of the Commission of November 20, 2002 extending the deadline in accordance with Article 8 paragraph 2 of Council Directive 91/414 / EEC and on the non-inclusion of certain active substances in Annex I of this directive and the revocation of Approvals of plant protection products with these active ingredients (PDF) .
- ↑ General Directorate Health and Food Safety of the European Commission: Entry on Quinalphos in the EU pesticide database ; Entry in the national registers of plant protection products in Switzerland , Austria and Germany ; accessed on March 12, 2016.


