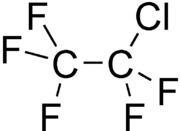
Chloropentafluoroethane
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Chloropentafluoroethane | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 ClF 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
non-flammable, colorless and odorless gas (with a higher concentration, sweet, ethereal odor) |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 154.47 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
7.10 kg m −3 (at 0 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−99.4 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−39.1 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
796 k Pa (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
poor in water (250 mg l −1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.2678 (−42 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
Switzerland: 1000 ml m −3 or 6400 mg m −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Global warming potential |
8516 (based on 100 years) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
−1118.8 kJ / mol |
||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||||||||
Chloropentafluoroethane is a chemical compound from the group of fully halogenated chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) that was used as a refrigerant and propellant . It is considered harmful to the ozone layer .
properties
Chloropentafluoroethane is a colorless, odorless (in higher concentrations a sweet, ethereal odor) gas. It decomposes when heated to a great extent, which can produce halogen compounds such as hydrogen chloride and hydrogen fluoride, as well as dioxins . Chloropentafluoroethane has a heat capacity of 0.116 kJ / (mol K).
safety instructions
As with all CFCs, the decomposition (through intense heat) of chloropentafluoroethane forms corrosive substances ( hydrochloric acid , hydrofluoric acid ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Entry on chloropentafluoroethane in the GESTIS material database of the IFA , accessed on May 17, 2015 (JavaScript required)
- ↑ geocities.jp: Chloropentafluoroethane (CFC-115)
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-110.
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 76-15-3 or chloropentafluoroethane ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ G. Myhre, D. Shindell et al .: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis . Working Group I contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report. Ed .: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . 2013, Chapter 8: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing, pp. 24-39; Table 8.SM.16 ( PDF ).
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-21.
- ↑ Swiss Federal Council: Ordinance on environmentally hazardous substances (Substance Ordinance, StoV) (PDF; 90 kB), amendment of April 30, 2003.
- ↑ Airliquide: Chloropentafluoroethane (R115) .

