Cimmeria (continent)

Cimmeria or Kimmeria is a prehistoric Peri- Gondwana element of the last supercontinent Pangea . Cimmeria is from the carbonic Hun super terran , the min. Existed 50 million years before in what was then Palaeotethys .
The continental fragment may have already dissolved around the Permian-Triassic border (250 mya ), but at least in the Jura (around 170 mya) - i.e. 20 to 100 million years before the dissolution of Pangea, from the southern part - the old southern continent of Gondwana - from and rotated in the Tethys in the area of today's Carpathians . The mountains of the Cimmerian fold belt - in particular the western Balkan Kimmeriden - contain mainly eroded rocks of the Variscan and the Cadomian crust of Cimmeria that is enclosed there and are now geological zones of the Alpine mountain belt .
Volcanic islands or parts of the continental plate
The microcontinent Cimmeria can also be seen as the westernmost island of the different, namely volcanic, Cimmerian island arc north of the deep sea trench Tethysgraben - today's Turkey , Iran , Caucasus , Tibet , Indochina . The different views of geology are also clear here: other authors see - in contrast to the view presented above - the entire island chain Cimmeria Superterran as Peri-Gondwana elements. This perspective is explained in more detail below:
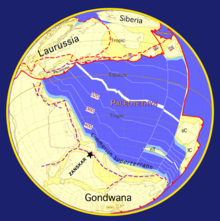
300 mya
The Cimmerian Plate was still connected to India and thus Gondwana during the Upper Precambrian and Paleozoic Era . The Palaeotethys separated them from Laurasia. During this period the northern part of India was influenced by a late phase of the so-called Cambrian-Ordovician Pan-African Event or Pan-African Mountain Formation or (?) Cadomian Orogeny , which is characterized by different stratifications of Ordovician continental conglomerates and underlying Cambrian marine sediments. The numerous granite-like intrusions that are dated around 500 mya are also attributed to this event.
250 mya
A rift valley in the early Carboniferous begins to separate Cimmeria from the Indian continental plate. During the Permian this fracture zone develops into a new ocean, the Tethys . The Cimmerian Terran migrate northwards towards Laurasia and today form parts of Iran, Afghanistan and Tibet.
190 mya and 100 mya
The Cimmerian Plates collided with Laurasia about 190 million years ago. This clash formed the Cimmerian fold belt with gradual closure of the Palaeotethys . It was not until 100 million years later that the Indian tectonic plate began its rapid north movement with an average of 16 cm / year, and first generated the Tethys Trench and subsequently the Asian part of the Alpine mountain belt from the Cretaceous to the Pleistocene . Even today, India is pushing at a distance of 2400 km at 5 cm / year and a counterclockwise rotation of 33 degrees in the direction of the continental plates Kazakhstan , Siberia , southern China and northern China . The continental crust of India and the cratons of north and south Tibet as well as the other Cimmerian terranes were and are being pressed together and parts lifted in complex accretion , folding and subduction processes . Part of this now alpidisch called orogeny is the Himalayas .
Sources, references
- Map of mountain formations in Europe
- The Cimmerian Islands along the Tethys Trench in the Upper Jurassic. The Palaeotethys is getting narrower. Cimmeria is located southeast of Baltica.
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento of the original from September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Shadows of old continents ( Memento from August 28, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ see graphics, en: Cimmerian Plate , en: Cimmeria (continent)