Sodium tetracarbonyl ferrate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
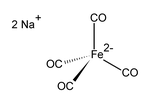
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Sodium tetracarbonyl ferrate | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Collman's reagent |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Na 2 [Fe (CO) 4 ] | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 213.87 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Sodium tetracarbonyl ferrate (II) is an inorganic compound with the formula Na 2 [Fe (CO) 4 ]. It is an air-sensitive, colorless solid, the tetrahydrofuran adduct of which is used in organic chemistry under the name of Collman's reagent for the synthesis of aldehydes from alkyl bromides . Collman called the compound the transition metal equivalent to Grignard compounds .
presentation
Sodium tetracarbonyl ferrate (II) can be obtained by reducing iron pentacarbonyl with sodium dissolved in liquid ammonia .
Alternatively, sodium amalgam in tetrahydrofuran can be used as a reducing agent. With this method, the resulting complex can be converted directly into the further reaction steps in a one-pot reaction .
use
The compound can be used to convert primary alkyl bromides into the corresponding aldehydes. In the first step, the alkyl complex is formed with the formation of sodium bromide .
The aldehyde is released by adding triphenylphosphine and then acidifying it with acetic acid .
The resulting primary alkyl complex can be converted into the acyl complex by triphenylphosphine and into the carboxylic acid by oxidation with oxygen and subsequent acidification . The acyl complex is converted into the carboxylic acid chlorides by oxidation with halogens .
If, instead of alkyl bromides, acid chlorides are reacted with sodium tetracarbonyl ferrate, the resulting acyl complexes release the aldehyde through reaction with mineral acids.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on Collman's reagent. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on Dec 14, 2015.
- ^ A b Robert J. Angelici: Inorganic Syntheses, Reagents for Transition Metal Complex and ... John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 0-470-13294-9 , pp. 206 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ James P. Collman: Disodium tetracarbonylferrate, a transition metal analog of a Grignard reagent. In: Accounts of Chemical Research. 8, 1975, pp. 342-347, doi : 10.1021 / ar50094a004 .
- ↑ H. Behrens, R. Weber: On the knowledge of the chemistry of metal carbonyls in liquid ammonia. I. About the reactions of the carbonyls of iron and cobalt with alkali metals. In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry. 281, 1955, pp. 190-198, doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19552810309 .
- ↑ Manning P. Cooke: Facile conversion of alkyl bromides into aldehydes using sodium tetracarbonylferrate (-II). In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 92, 1970, pp. 6080-6082, doi : 10.1021 / ja00723a056 .
literature
Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis , 1999–2013, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., entry for Disodium Tetracarbonylferrate (II)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {[Fe (CO) _ {5}] + 2 \ Na \ rightarrow \ Na_ {2} [Fe (CO) _ {4}] + CO}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f14a510e38feb52afc02083e7745e9805b498b2f)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {Na_ {2} [Fe (CO) _ {4}] + RBr \ \ rightarrow \ Na [Fe (R) (CO) _ {4}] + NaBr}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9163daba3c328ef791fd305839695e014038d570)
![{\ displaystyle \ mathrm {Na [Fe (R) (CO) _ {4}] + PPh_ {3} \ \ rightarrow \ Na [Fe (C (= O) R) (CO) _ {3} (PPh_ { 3})]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31e30f2e4151043d966418a14772994d80ce8211)