Cross River National Park
| Cross River National Park | ||
|---|---|---|
| The Kwa waterfalls | ||
|
|
||
| Location: | Nigeria | |
| Specialty: | Region Cross River | |
| Next city: | Ikom , Calabar | |
| Surface: | 4000 km² | |
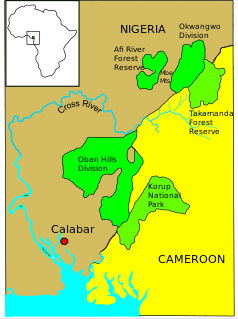
| The Cross River National Park with the Okwangwo Sector in the north and the Oban Sector in the south. | ||
The Cross River National Park ( English Cross River National Park , (CRNP)) is located in southeastern Nigeria and covers an area of 4000 km² in the state of Cross River . It consists of two geographically separated protection zones, the Oban sector and the Okwangwo sector. These include the last contiguous lowland rainforest areas in Nigeria, which reach a height of 40 to 50 meters above the ground. Studies have shown that this rainforest has an evolutionary history of around 60 million years. Both sectors of the national park form biosphere corridors with the national parks in Cameroon and these become biodiversity hotspots designated.
Flora and fauna censuses show that 119 species of mammals , 49 species of fish and about 950 species of butterflies live in the two sectors of the national park . The national park is of particular importance for the protection of primates in Nigeria, as 18 of the 23 species known in Nigeria live within the park boundaries.
Both areas can be reached via the federal highway A4, Calabar - Ikom , or via the Cross River .
Oban Sector
The Oban sector covers an area of approx. 3000 km² and lies on the border with Cameroon and forms a biosphere corridor with the Korup National Park . It has been on the list of proposals for inclusion in UNESCO World Heritage since 1995 under the title Oban Hills / Korup . This sector is divided into two administrative areas, Oban East and Oban West. The terrain of the sector is determined by the topography of the Oban Hills . They are described as hilly to mountainous and reach up to 1000 meters above sea level. The northern part of the sector lies in the water catchment area of the Cross River, the southern part in the catchment area of the rivers Calabar, Kwa and Korup. The rainy season lasts from March to November and reaches its peak in the summer months, with the arrival of the West African monsoons with an annual rainfall of 3500 mm.
The flora of the Oban sector includes 1,568 distinct species of vascular plants , of which 77 are endemic to Nigeria. The vegetation is determined by a rainforest, in which the tree species Berlinia confusa , Coula edulis , Hannoa klaineana , Klainedoxa gabonensis , Khaya ivorensis and Lophira alata form the dominant species. The sector is also rich in epiphytic growing ferns and orchids .
From the mammals among others, the coming forest elephant ( Loxodonta cyclotis ), the chimpanzee ( Pan troglodytes ), the drill ( Mandrillus leucophaeus ), the Nigeria-moustached guenon ( Cercopithecus sclateri ) and the Preuss's red colobus ( Piliocolobus preussi ) ago. There are around 349 species of avifauna . The Oban sector is an important refuge of Rachel Weber ( Malimbus racheliae ) Graukehlschnäppers ( Myioparus griseigularis ), Eastern Haarbülbül ( Criniger chloronotus ) Xavierbülbül ( Phyllastrephus xavieri ) Fledermausaars ( Macheiramphus alcinus ), Black armpit eagle ( Aquila africanus ), Crested Guinea Fowl ( Guttera pucherani ), eye rail ( Canirallus oculeus ), olive cuckoo ( Cercococcyx olivinus ), yellow-cheeked trogon ( Apaloderma aequatoriale ) and the lyre-tail honey indicator ( Melichneutes robustus ).
Okwangwo Sector
The Okwangwo Sector is about 50 km northeast of the Oban Sector in the Sankwala and Mbe Mountains . The sector covers an area of approx. 1000 km² and forms a biosphere corridor with the Afi Mountain Wildlife Sanctuary , Mbe Mountains Community Wildlife Sanctuary and Takamanda National Park in Cameroon. The terrain of the sector is mountainous, reaching heights of up to 1700 meters in the north and 1000 meters above sea level in the southwest. In this area lie the sources of the Oyi, Bemi and Okon rivers, all tributaries of the Cross River. The annual precipitation can be up to 4280 mm, whereby there is a marked separation between rainy and dry season .
The flora in this sector includes 1545 registered vascular plants of different families, of which the Anceistocladus korupensis and Prunus africana are of particular importance in the treatment of the immunodeficiency disease AIDS and prostate cancer . The vegetation is determined by large-scale flat rainforests and grass savannahs . New species of plants have been repeatedly found and described in this sector in recent years. About 75 plant species are of economic or medicinal importance for the local population.
The sector is an important refuge for the Cross River gorilla ( Gorilla gorilla diehli ) and the Buntkopf rockhopper ( Picathartes oreas ), both of which are threatened with extinction.
Web links
- NG007 Cross River National Park: Oban Division on BirdLife (English)
- NG010 Cross River National Park: Okwangwo Division on BirdLife (English)
- The National Park on Nigeria National Park Service (English)
- World Database on Protected Areas - Cross River National Park (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ UNESCO TenttiveList (English)