Decalin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
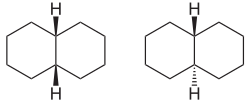
|
|||||||||||
| cis -decalin (left) and trans -decalin (right) | |||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||
| Surname | Decalin | ||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 | ||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a camphor or menthol odor |
||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||
| Molar mass | 138.25 g mol −1 | ||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||
| density |
|
||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
||||||||||
| boiling point |
|
||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
1.3 h Pa (20 ° C, mixture of isomers) |
||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water (6 mg l −1 at 25 ° C) |
||||||||||
| Refractive index |
|
||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||
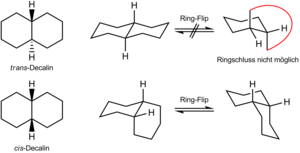
Decalin (also decahydronaphthalene , perhydronaphthalene , bicyclo [4.4.0] decane ) is a colorless liquid. It is produced by the catalytic hydrogenation of naphthalene and used as a solvent (e.g. in shoe polish ). Depending on the linkage geometry of the two cyclohexane rings, there are two isomeric decalins, the cis decalin (hydrogen atoms on the bridgehead carbon atoms are cis to each other) and the trans decalin. Decalin is a bicyclic alkane and belongs to the superordinate group of hydrocarbons .
The technical product is usually a mixture of the isomers.
properties
physical and chemical properties
The colorless, hardly volatile liquid has a camphor-like odor. The technical mixture of isomers melts at around −40 ° C, boils at around 190 ° C and is flammable. Configuration The two isomers have different physical properties, so that lies melting point of the trans isomer at -30 ° C, the boiling point at 187 ° C and the density 0.8700 g / ml; the cis isomer melts at −43 ° C, boils at 196 ° C and has a density of 0.8963 g / ml. Due to the difference in boiling point, Walter Hückel was able to separate the two isomers from one another by careful distillation in 1925. The trans form is 8.4 kJ / mol lower in energy than the cis form. Decalin is almost insoluble in water and is miscible with most hydrocarbons , acetone and benzene .
Conformation
cis -Decalin has two chair conformers that are in equilibrium via a ring flip . In both conformers, the second six-membered ring is bound axially on one side and equatorially on the other, so that both ring-flip conformers are stable. In the case of trans -Decalin, the second six-membered ring is connected to the stable chair conformer via two equatorial bonds. After a hypothetical ring flip, these bonds would be axial. This conformation is not realized because the second six-membered ring would have to be expanded too far. trans -decalin therefore has only one chair conformer, while cis -decalin occurs in two enantiomeric chair conformers, which quickly convert into one another at room temperature and represent an inseparable racemic form .
The two conformational forms were predicted by Ernst Mohr and confirmed by Walter Hückel around 1925.
Safety instructions / toxicology
Decalin has an irritant effect on the skin and mucous membranes, is easily absorbed through the skin and is slightly hazardous to water (WGK 1).
Decalin was included by the EU in 2012 in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation in the Community's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ). The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The reasons for the uptake of decalin were concerns about high (aggregated) tonnage and the dangers arising from a possible assignment to the group of PBT / vPvB substances. The re-evaluation took place from 2012 and was carried out by Finland .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Entry on Decalin in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-134.
- ↑ Beyer-Walter, Textbook of Organic Chemistry, S. Hirzel Verlag Stuttgart.
- ↑ Entry on Dekalin. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on October 1, 2014.
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Organic Chemistry , 2nd revised edition, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, p. 107, ISBN 3-342-00280-8 .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): decahydronaphthalene , accessed on March 26, 2019.