Di- tert-butyl dicarbonate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
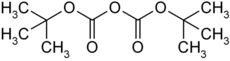
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Di- tert-butyl dicarbonate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 18 O 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid or liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 218.25 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.02 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
20-23 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
56–57 ° C (0.7 h Pa ) |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Di- tert -butyl dicarbonate [colloquially in the laboratory also known as Boc anhydride (Boc 2 O) or Diboc ] is a liquid, chemical compound which structurally belongs to both esters and acid anhydrides .
use
The main use of di- tert -butyl dicarbonate is the introduction of the tert- butyloxycarbonyl group ( Boc group ), one of the most commonly used protecting groups in organic chemistry. It is the most widely used chemical to protect amino functions in chemical reactions, especially in peptide and glycopeptide chemistry.
In addition, di- tert-butyl dicarbonate can be used to convert primary aliphatic and aromatic amines into the corresponding isocyanates in the presence of catalytic amounts of 4- (dimethylamino) pyridine (DMAP) .
Manufacturing
Di- tert -butyl dicarbonate is produced worldwide using two processes: on the one hand by the reaction of sodium or potassium tert -butoxide with phosgene or phosgene derivatives and on the other hand the catalytic reaction of sodium tert -butoxide with carbon dioxide . The preparation from potassium tert -butanolate and phosgene proceeds according to the following scheme:
cleavage
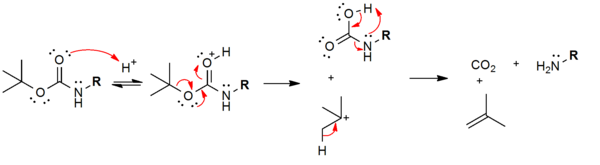
In contrast to the Cbz protective group , the Boc protective group can already be split off by means of dilute aqueous acid (≈3 M HCl) via the E1 step. The cleavage products are CO 2 and isobutene , both of which are volatile and so do not contaminate the deprotected amine. Boc is extremely stable towards bases, even towards OH - , since the carbonyl group is sterically hindered.
The mechanism of the split:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (PDF) from Merck , accessed on January 19, 2011.
- ↑ a b Entry on di-tert-butyl dicarbonate in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2018(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Hans-Joachim Knölker, Tobias Braxmeier, Georg Schlechtingen: A Novel Method for the Synthesis of Isocyanates Under Mild Conditions. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 34, 1995, pp. 2497-2500, doi : 10.1002 / anie.199524971 .
- ↑ Barry M. Pope, Yutaka Yamamoto, and D. Stanley Tarbell: Dicarbonic acid, bis (1,1-dimethylethyl) ester In: Organic Syntheses . 57, 1977, p. 45, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.057.0045 ; Coll. Vol. 6, 1988, p. 418 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, Stuart Warren: Organic Chemistry. Oxford University Press; 2nd edition, 2012, p. 558.