Dichloroacetaldehyde
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dichloroacetaldehyde | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
2,2-dichloroacetaldehyde |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 2 Cl 2 O | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 112.94 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.4 g / ml |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−50 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
88 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
67 mbar (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
easily in water (140 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dichloroacetaldehyde is a chemical compound from the group of aldehydes . It is next to the monochloroacetaldehyde and trichloroacetaldehyde one of three possible chlorinated acetaldehyde.
Extraction and presentation
Dichloroacetaldehyde, by chlorination of acetaldehyde or paraldehyde be won. The hypochlorination of 1,2-dichloroethylene using chlorine and water provides pure dichloroacetaldehyde.
properties
Dichloroacetaldehyde is a volatile liquid that is easily soluble in water, forming hydrate. In water, a diol, also known as monohydrate, chemically 2,2-dichloro-1,1-ethanediol, is formed. This compound forms colorless crystals that melt between 35 and 50 ° C and boil at 85 to 95 ° C.
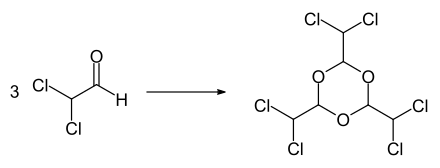
The compound decomposes when heated. In the presence of Lewis acids such as antimony trichloride , iron (III) chloride , aluminum trichloride , tin (IV) chloride or boron trifluoride , the trimer hexachloroparaldehyde (2,4,6-tris (dichloromethyl) -1,3,5-trioxane) can be obtained. The trimer forms colorless crystals that melt at 131–132 ° C. At the boiling point of 210–220 ° C, dichloroacetaldehyde slowly regresses.
use
Dichloroacetaldehyde is used in the production of other chemical compounds such as mitotane . The condensation with chlorobenzene gives p , p ' -Dichloro-1,1-diphenyl-2,2-dichloroethane , which was previously used as an insecticide .
safety instructions
The vapors of dichloroacetaldehyde can form an explosive mixture with air ( flash point 60 ° C).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on dichloroacetaldehyde in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 8, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d e f Jira, R .; Kopp, E .; McKusick, BC; Röderer, G .; Bosch, A .; Fleischmann, G .: Chloroacetaldehydes in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry , 2012 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a06_527.pub2 .
- ↑ Entry on dichloroacetaldehyde in the Hazardous Substances Data Bank , accessed on April 21, 2015.
- ↑ Wiley-VCH: Ullmann's Fine Chemicals, 3 Volume Set: . John Wiley & Sons, 2014, ISBN 978-3-527-68359-8 , pp. 133 ( limited preview in Google Book search).