Diphenic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Diphenic acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 10 O 4 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray-white powder, monoclinic prisms or plates, needles |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 242.23 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.2917 g · cm -3 |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
228 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Diphenic acid (HOOCC 6 H 4 C 6 H 4 COOH) is an aromatic chemical compound . The structure consists of two benzene rings , each with a carboxy group (-COOH) attached in the ortho position . The acid forms an internal anhydride with a seven-membered ring fused to the two benzene rings ; the anhydride has a melting point of 219 ° C.
Extraction and presentation
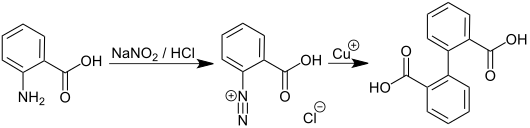
Diphenic acid can be obtained from anthranilic acid by diazotization and subsequent action of copper (I) ions:
It is also accessible starting from phenanthrene . Here, peroxyacetic acid is first produced from acetic acid and 90% hydrogen peroxide:
This is then implemented with phenanthrene:
If phenanthrene is treated with oxidizing agents (e.g. hydrogen peroxide , chromium (VI) oxide , potassium dichromate , potassium permanganate ), 9,10-phenanthrenequinone is formed and, through further oxidation, diphenic acid.
If 9,10-phenanthrenequinone is boiled with alcoholic potash , the potassium salt of diphenic acid is formed.
Diphenic acid is also formed by photooxidation from 9,10-phenanthrenequinone.
use
Diphenic acid can be used to produce polyester and alkyd resins .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on diphenic acid. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 7, 2016.
- ↑ a b c d Data sheet Diphenic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on February 24, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ^ Carl Yaws: Thermophysical Properties of Chemicals and Hydrocarbons. William Andrew, June 20, 2014, ISBN 978-0-323-29060-9 , p. 325.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 96th edition. (Internet version :), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-48.
- ^ D'Ans-Lax: paperback for chemists and physicists. 4th edition, Volume 2, Springer Verlag, 1982, ISBN 3-540-12263-X .
- ^ ER Atkinson, HJ Lawler .: Diphenic Acid In: Organic Syntheses . 7, 1927, p. 30, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.007.0030 ; Coll. Vol. 1, 1941, p. 222 ( PDF ).
- ^ William F. O'Connor, Emil J. Moriconi: 2,2′-Diphenic Acid from Phenanthrene . In: Industrial & Engineering Chemistry . tape 45 , no. 2 , February 1953, p. 277-281 , doi : 10.1021 / ie50518a020 .
- ^ CR Noller: Textbook of Organic Chemistry. Springer-Verlag, 1960, ISBN 978-3-642-87325-6 , p. 635, doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-642-87324-9
- ↑ Hans Meyer: Synthesis of the carbon compounds: First part: Open chains and isocycles. Springer-Verlag, 1938, ISBN 978-3-7091-3245-6 , p. 1170.
- ↑ Gustav Schultz: Die Chemie des Steinkohlentheers: Bd. The raw materials. Friedrich Vieweg and son, 1886.
- ↑ A. Coehn, G. Jung, J. Daimer: Photochemie and Photographic Chemical Science. Springer Vienna, 1926, ISBN 978-3-7091-5255-3 , p. 136, doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-7091-5403-8
- ^ Heinz-Gerhard Franck, Jürgen W. Stadelhofer: Industrial aromatic chemistry: Raw materials-process-products. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1987, ISBN 978-3-662-07875-4 , p. 377, doi: 10.1007 / 978-3-662-07875-4