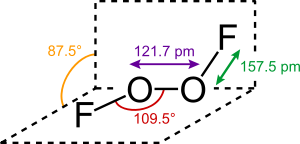
Dioxygen difluoride
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Dioxygen difluoride | ||||||||||||
| other names |
Fluoroperoxide |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | O 2 F 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
brown gas |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 70.0 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
||||||||||||
| density |
|
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−163.5 ° C |
||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−57 ° C |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Oxygen difluoride is a chemical compound from the group of fluorides , more precisely the oxygen fluorides .
Extraction and presentation
Oxygen difluoride can be obtained by reacting oxygen and fluorine using an electrical discharge . The first synthesis goes back to Otto Ruff in 1933.
properties
Oxygen difluoride is brown as a gas, cherry-red as a liquid and orange-yellow in the solid state. The structure of the solid corresponds to that of hydrogen peroxide .
It is unstable (decomposition from −95 ° C) and a strong oxidizing and fluoridating agent . It oxidizes chlorine to chlorofluoride and chlorotrifluoride , and hydrogen sulfide to sulfur hexafluoride .
use
Oxygen difluoride serves as a fluorinating agent in order to convert neptunium or plutonium compounds at low temperatures to the hexafluorides .
Neptunium dioxide and tetrafluoride are almost completely converted to volatile neptunium hexafluoride by dioxygen difluoride (O 2 F 2 ) . This is possible both in gas-solid reactions at moderate temperatures and in liquid anhydrous hydrogen fluoride at −78 ° C:
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g G. Brauer; Handbook of preparative inorganic chemistry, F. Enke Verlag 1978, ISBN 978-3-432-26081-5 .
- ↑ a b Entry on Oxygen Fluoride. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 12, 2017.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Otto Ruff , W. Menzel: "Neue Oxerstofffluoride: O 2 F 2 und OF", Journal for inorganic and general chemistry , 1933 , 211 (1–2), pp. 204–208 ( doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19332110122 ) .
- ^ AJ Bridgeman, J. Rothery: "Bonding in mixed halogen and hydrogen peroxides", Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions , 1999 , pp. 4077-4082 ( doi : 10.1039 / a904968a ).
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 .
- ^ Streng AG: The Chemical Properties of Dioxygen Difluoride . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . 85, No. 10, 1963, pp. 1380-1385. doi : 10.1021 / ja00893a004 .
- ↑ Ralf Steudel : Chemistry of non-metals ; ISBN 978-3-11-012322-7 .
- ^ P. Gary Eller, Larned B. Asprey, Scott A. Kinkead, Basil I. Swanson, Richard J. Kissane: "Reactions of Dioxygen Difluoride with Neptunium Oxides and Fluorides", in: Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 1998 , 269 ( 1-2), pp. 63-66 ( doi : 10.1016 / S0925-8388 (98) 00005-X ).
Web links
- Entry to perfluoroperoxides . In: P. J. Linstrom, W. G. Mallard (Eds.): NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 . National Institute of Standards and Technology , Gaithersburg MD
- Things I Won't Work With: Dioxygen Difluoride - Blog post (English) by chemist Derek Lowe on the devastating properties of O 2 F 2