Embutramide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
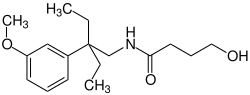
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Embutramide | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 17 H 27 NO 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 293.41 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Embutramide is a drug that has a strong anesthetic ( narcotic ) effect. It is only in fixed combination with other drugs for euthanasia ( euthanasia used) of animals.
Mechanism of action
Embutramide is a derivative of γ-hydroxybutyric acid and is able to cross the blood-brain barrier . It causes a long and deep loss of consciousness ( hypnosis ) and has a very strong dampening effect on the respiratory center in the brain stem . Its narrow therapeutic range makes it unusable for general anesthesia . In experiments on dogs, higher doses caused respiratory arrest and severe cardiac arrhythmias.
For the safe effect, Embutramid must be combined with other suitable active ingredients. For example, the muscle relaxant mebezonium causes permanent depolarization on the motor end plate and permanently relaxes the skeletal and thus also the respiratory muscles - breathing stops. The chloroquine used in human medicine for the treatment of malaria dampens the heart activity in dogs and leads to a drop in blood pressure through vasodilation. Local anesthetics such as tetracaine or lidocaine prevent local pain reactions, which can occur in particular with injections into the lungs, but also with intravenous administration. Intravenously, tetracaine and lidocaine have a depressive effect on the heart and the central nervous system.
An appropriate combination of active ingredients causes an immediate loss of consciousness, respiratory and cardiac arrest.
Commercial preparations
A combination preparation with 200 mg embutramide, 50 mg mebezonium and 5 mg tetracaine per ml is sold worldwide by Intervet ( MSD group of companies ) or its sales partners under the trade names T 61 (for example in D , A , CH , NL ) or Tanax ( for example in I ). A dimethylformamide- water mixture is used as the solvent for the medicinal substances.
A combination product containing 135 mg embutramide, 45 mg chloroquine phosphate and 1.9 mg lidocaine per ml has been approved in the USA under the name Tributame Euthanasia Solution ( Teva Animal Health) only for dogs .
application
T 61 may only be used by veterinarians and as a means of killing in the context of animal experiments. The use of food-producing animals is prohibited in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 470/2009 . The agent is used intravenously (possibly intracardially ), as this is the only way to take into account the different pharmacokinetics of the ingredients. In exceptional cases, if there is no intravenous access, T 61 is also used intrapulmonary (into the lungs) or intraperitoneally (into the abdominal cavity), but other drugs should be preferred here.
T 61 works in a few seconds to minutes. In the case of intravenous administration, it is important to ensure that the entire dose is correctly injected into the vein. Under unfavorable circumstances or through incorrect use, conscious suffocation can occur, which means an excruciating death and can drag on for hours. The use of T 61 as the sole means of euthanasia is therefore controversial. In order to safely achieve the goal of painless killing, veterinarians administer a strong dose of anesthetic before using T 61. The contraindications of intrapulmonary and intracardiac administration for unconscious animals have been expanded to include intravenous administration in European countries (e.g. D, A, CH, I) on the initiative of the Federal Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety (BVL), so that T 61 generally only may be used in unconscious (anesthetized) animals.
Use on pregnant animals is also a contraindication .
Occasional cases of human abuse by suicides have been reported.
With the preparation Tributame Euthanasia Solution , an early onset of respiratory arrest, as long as the dog is still conscious, is to be avoided by dispensing with a muscle-relaxing component. The product is not suitable for euthanizing cats.
Web links
- Entry on Embutramid at Vetpharm, accessed on August 11, 2012.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on embutramid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on July 10, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b c d Freedom of Information Summary: NADA 141-245. Tributame Euthanasia Solution (embutramide / chloroquine phosphate / lidocaine). (PDF; 68 kB), May 2005 (English).
- ↑ M. Giorgi, S. Bertini: TANAX (T-61) - an overview . In: Pharmacol. Res. , 41 (4), 2000, pp. 379-383. PMID 10704259
- ↑ Technical information T 61 solution for injection . Intervet Deutschland GmbH, as of September 2010.
- ↑ bvl.bund.de: Adaptation of the authorization conditions for veterinary medicinal products T61 ( Memento of December 28, 2015 in the Internet Archive ), November 3, 2010.
- ↑ Jim E. Riviere, Mark G. Papich: Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics . John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-8138-2061-3 , pp. 406 ( limited preview in Google Book search).