Tetracaine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
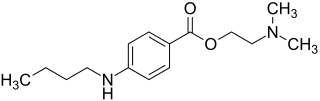
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Tetracaine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 15 H 24 N 2 O 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white to slightly yellowish waxy substance (tetracaine) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of action |
Blockade of voltage-dependent sodium channels |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 264.37 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tetracaine is used as a surface anesthetic for mucous membranes - for example for small operations in the mouth or nose. The effect lasts for several hours. It is about ten times more effective than procaine , but also ten times more toxic, which is why the maximum single dose of 20 mg must not be exceeded when used. If there are injuries to the mucous membrane, the absorption takes place very quickly, so that there is a risk of overdosing with poisoning. Lidocaine , which has the same mechanism of action as tetracaine, is therefore used more frequently .
After being applied to the nasal mucosa, tetracaine reaches the rami alveolares ( superior anterior alveolar nerve and superior alveolar nerve medius ) which run underneath and which supply the teeth of the upper jaw with sensitivity. In a fixed combination with the vasoconstricting oxymetazoline it can be used as a nasal spray for minor procedures in dentistry for local anesthesia in the upper jaw.
Tetracaine was developed by employees of the Hoechster Farbwerke belonging to the IG Farben group and was first marketed in 1931 under the name Pantocain as a surface anesthetic agent.
Trade names
Ophtocain (D), Gingicain (D), Tetracaine SDU Faure 1% (CH)
- with lidocaine : Pliaglis (D, A, CH), Rapydan (A, D)
- with oxymetazoline : Kovanaze (USA)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Entry on tetracaine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on August 18, 2011.
- ↑ a b Datasheet Tetracaine from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 24, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ FDA Approved Drug Products - Kovanaze