Acetic acid n- butyl ester
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
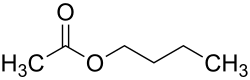
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Acetic acid n-butyl ester | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 12 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, fruity smelling liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 116.16 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
0.88 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−77 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
127 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.3941 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
DFG / Switzerland: 100 ml m −3 or 480 mg m −3 |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Acetic acid n -butyl , and butyl acetate or Butylethanoat , is a clear, colorless solvent with a rather pleasant, fruity odor. It is the ester of acetic acid with 1-butanol . In addition to this, the esters of the isomeric butanols acetic acid sec- butyl ester , acetic acid isobutyl ester and acetic acid tert-butyl ester are important.
Extraction and presentation
On an industrial scale, n-butyl acetate is produced by the acid-catalyzed esterification of acetic acid with n-butanol at temperatures of 80 - 120 ° C. Acid ion exchange resins are usually used as the catalyst . On a laboratory scale, p-toluenesulfonic acid is usually used as the catalyst .
According to the principle of Le Chatelier , separation of the water produced or the removal of the ester shifts the equilibrium to the product side (see also the law of mass action ).
properties
Acetic acid n- butyl ester is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor. The melting temperature is −76 ° C. The boiling point under normal pressure is 126 ° C. The compound forms an azeotropic mixture with water . At normal pressure and with a water content of 26.7% by mass, the azeotropic boiling point is 90.2 ° C.
Thermodynamic properties
The vapor pressure function results according to Antoine according to log 10 (P) = A− (B / (T + C)) (P in bar, T in K) with A = 4.26803, B = 1440.231 and C = −61.362 in the temperature range from 332.9 to 399.2 K.
Compilation of the most important thermodynamic properties property Type Value [unit] Remarks Standard enthalpy of formation Δ f H 0 liquid
Δ f H 0 gas−609.6 kJ mol −1
−566.0 kJ mol −1as a liquid
as a gasEnthalpy of combustion Δ c H 0 liquid −3467.0 kJ mol −1 Heat capacity c p 225.11 J mol −1 K −1 (25 ° C) as a liquid Critical temperature T c 575.4 K Critical pressure p c 30.9 bar Enthalpy of evaporation Δ V H 0 43.89 kJ mol −1 at normal pressure boiling point
The temperature dependence of the evaporation enthalpy can be calculated according to the equation Δ V H 0 = A e (−βT r ) (1 − T r ) β (Δ V H 0 in kJ / mol, T r = (T / T c ) reduced temperature ) with A = 64.07 kJ / mol, β = 0.306 and T c = 579 K in the temperature range between 298 K and 358 K.
Safety-related parameters
n-Butyl acetate forms highly flammable vapor-air mixtures. The compound has a flash point of 27 ° C. The explosion range is between 1.2 vol.% (58 g / m 3 ) as the lower explosion limit (LEL) and approx. 8.5 vol.% As the upper explosion limit (UEL). The lower explosion point is 19.5 ° C. The maximum explosion pressure is 8.6 bar. The limit gap width was determined to be 1.02 mm. This results in an assignment to explosion group IIA. The ignition temperature is 390 ° C. The substance therefore falls into temperature class T2.
use
Acetic acid n- butyl ester is a widely used paint solvent. Among other things, this is found as a substitute for the banned dichloromethane in paint strippers . It is also used as a solvent in chemical laboratories.
It is also used in the histological analysis process, where it is used as an "intermediate". Before the histological organs are embedded in paraffin, an intermedium is inserted in between, since paraffin cannot mix with alcohol (the organ was previously placed in alcohol). The intermediate should also remove the last remaining water from the organ, otherwise it could have a disruptive effect when cutting the specimen. It would tear easier.
Due to its strong dissolving power , acetic acid n- butyl ester is also used as a component of nail polish removers and thinners. Acetic acid n- butyl ester is also found in apple juice and is used there as one of the reference substances for the apple aroma index .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Entry for CAS no. 123-86-4 in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 8, 2017(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ a b Entry on butyl acetate. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on November 26, 2018.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-76.
- ↑ Entry on N-butyl acetate in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limits - Current MAK and BAT values (search for 123-86-4 or n-butyl acetate ), accessed on November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Zuber Laurent, Bailer Oliver, Sander Stefan, Meierhofer Heinz: Process for the production of carboxylic acid esters by means of reactive distillation. In: European Patent Office. Sulzer Chemtech AG, August 26, 2009, accessed November 26, 2018 .
- ^ Klaus Schwetlick et al: Organikum . 24th edition. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2015, ISBN 978-3-527-33968-6 .
- ↑ a b H. Cheung, RS Tanke, GP Torrence: Acetic Acid. In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2005, doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a01_045 .
- ↑ V. Kliment, V. Fried, J. Pick: balance liquid-steam. XXXIII. Systems butyl acetate-phenol and water-phenol. In: Collect Czech Chem Commun . 29, 1964, pp. 2008-2015, doi: 10.1135 / cccc19642008 .
- ↑ a b c M. Șchiopu, O. Bot, V. Onu: Studiul termodinamic și cinetic al sistemului acetate de n-butil-apa. Nota I. In: Bul. Inst. Politehnic Iași. 7, 1961, pp. 115-118.
- ↑ E. Jimenez, L. Romani, Paz Andrade, MI, Roux-Desgranges, G., J.-PE Grolier: Molar excess heat capacities and volumes for mixtures of alkanoates with cyclohexane at 25 ° C. In: J. Solution Chem. 15, 1986, pp. 879-890.
- ↑ a b S. K. Quadri, AP Kudchadker: Measurement of the critical temperatures and critical pressures of some thermally stable or mildly unstable esters, ketones, and ethers. In: J. Chem. Thermodyn. 23, 1991, pp. 129-134, doi: 10.1016 / S0021-9614 (05) 80288-5 .
- ^ A b V. Majer, V. Svoboda: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford 1985, p. 300.
- ↑ a b c d e E. Brandes, W. Möller: Safety-related parameters. Volume 1: Flammable Liquids and Gases. Wirtschaftsverlag NW - Verlag für neue Wissenschaft, Bremerhaven 2003.
- ^ E. Brandes, M. Mitu, D. Pawel: The lower explosion point - A good measure for explosion prevention: Experiment and calculation for pure compounds and some mixtures. In: J. Loss Prev. Proc. Ind. 20, 2007, pp. 536-540, doi: 10.1016 / j.jlp.2007.04.028 .



